Question
Question: Compound 'A' of molecular formula \({{C}_{4}}{{H}_{10}}O\) on treatment with Lucas reagent at room t...
Compound 'A' of molecular formula C4H10O on treatment with Lucas reagent at room temperature gives compound 'B'. When compound 'B' is heated with alcoholic KOH, it gives isobutene. Compound 'A' and 'B' are respectively:
(A) 2-methyl-2-propanol and 2-methyl-2-chloropropane
(B) 2-methyl-1-propanol and 1-chloro-2-methylpropane
(C) 2-methyl-1-propanol and 2-methyl-2-chloropropane
(D) butan-2-ol and 2-chlorobutane
(E) none of the above
Solution
Write down the possible structures of organic compounds with molecular formula C4H10O. Now write the reaction of the possible compounds with Lucas reagent and note down the respective products that can possibly be compound 'B'. Now write the reaction of the products obtained from the previous reaction with alcoholic KOH and see which compound gives isobutene as the product.
Complete step by step answer:
Lucas reagent is a solution of anhydrous zinc chloride and hydrochloric acid. In this reaction, chloride replaces the hydroxyl group changing the compound from alcohol to alkyl chloride.
When an alkyl chloride reacts with alcoholic KOH, it leads to the elimination of the chloride ion and a hydrogen atom from the adjacent carbon atom i.e. β elimination.
We will try to write the chemical reaction of the above two reagents with the organic compounds given in the options.
Let us start with the first organic compound, the structure is given below:
2-methyl-2-propanol:
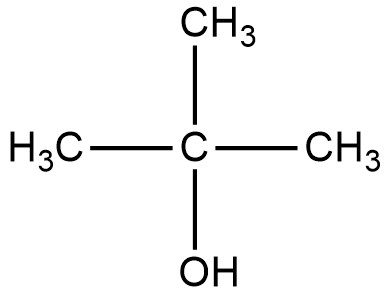
The reaction of Lucas reagent on 2-methyl-2-propanol gives 2-methyl-2-chloropropane.
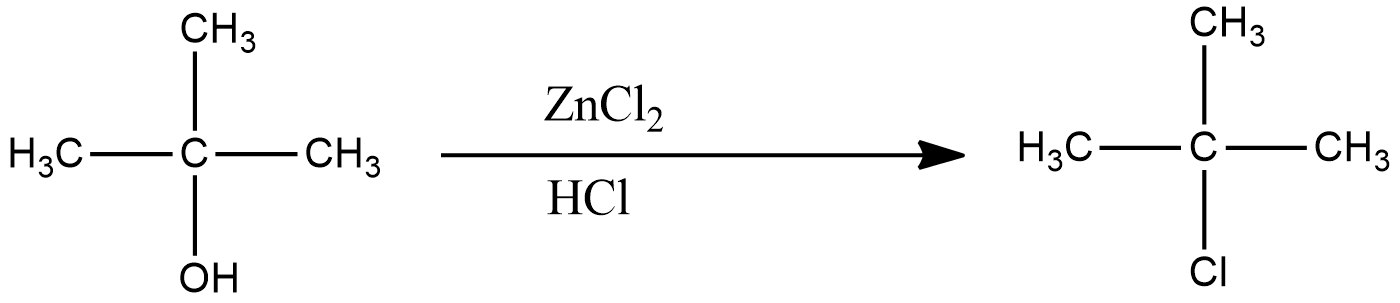
The reaction of 2-methyl-2-chloropropane gives 2-methylpropene.
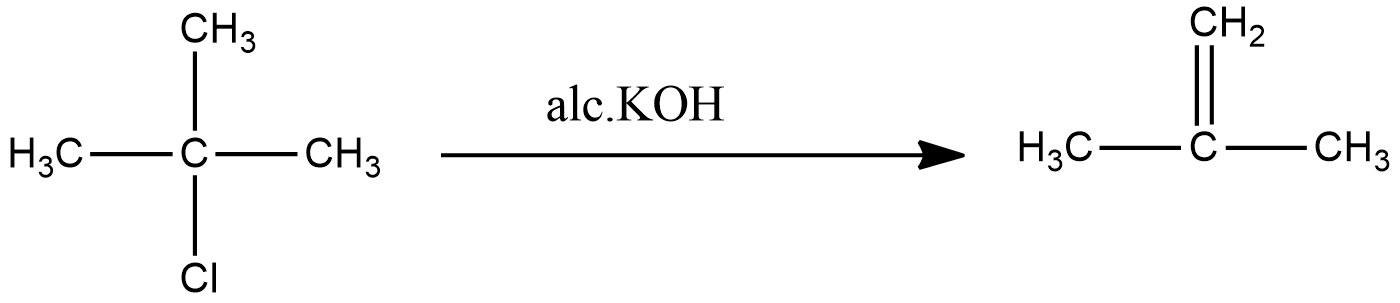
The common name for 2-methylpropene is isobutene. The final product matches with the final product mentioned in the question. Hence the compound (A) is 2-methyl-2-propanol and compound (B) is 2-methyl-2-chloropropane.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: The Lucas test for alcohols is a test to differentiate between primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. It is based on the difference in reactivity of the three classes of alcohols with hydrogen halides through SN1 reaction mechanism:
ROH + HCl → RCl + H2O
The above reaction happens instantly for tertiary alcohols. This is confirmed by the solution turning turbid. Primary alcohols react on long withstanding.
