Question
Question: Compound A (\[{{C}_{7}}{{H}_{15}}Br\] ) is not a primary alkyl bromide. It yields a single alkene (c...
Compound A (C7H15Br ) is not a primary alkyl bromide. It yields a single alkene (compound B) on being heated with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Hydrogenation of compound B yields 2,4−dimethylpentane. Identify compounds A and B.
A. 3-bromo-2,4-dimethylpentane and 2,4-dimethylpent-2-ene
B. 2-bromo-2,4-dimethylhexane and 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene
C. 3-bromo-2,4-dimethylhexane and 2,4-dimethylhex-2-ene
D. none of these
Solution
If the structural isomers of a compound are present and are reacted with some compound, they yield different products which may or may not be the isomers of each other. So we need to see all the possible structural isomers of compound A to be able to solve this question.
Complete step by step solution:
-The compound A is given to us as C7H15Br. We can draw the structure but for that, we first need to know the DBE of the compound. Here, the DBE will be calculated as C+1-2(15+1). This on solving gives us DBE=0. So the compound is saturated alkane with a halide which makes it alkyl halide.
-Now we need to find different positions of bromide that can be placed in heptane to form the desired products. The bromide is not primary as per the question and so we do not consider that.
-Both chain and position isomers are possible but we need to see the options first before drawing all the structures. Dimethyl groups are present in the options and so we need to make them. Then the carbon chain will have 2 less carbon atoms in it leading to pentane and butane.
-Hexane cannot be the chain because then, 2 methyl groups would not be able to get substituted and so we can easily eliminate options B and C. Only option A remains and we need to draw the structures according to that option only.
-Drawing the structures represented in the option A, we get the reactions as
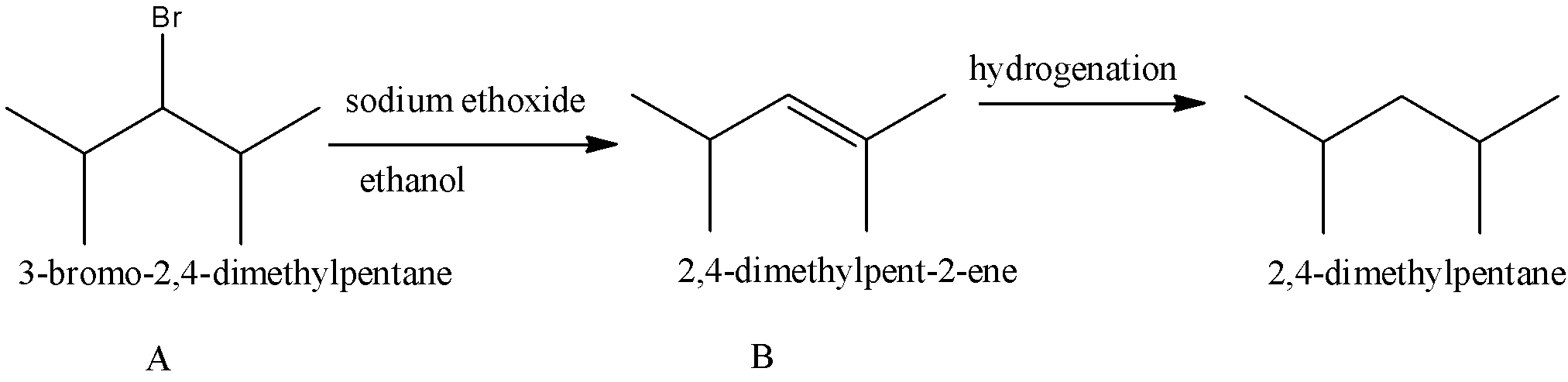
Therefore the correct option is A.
Note: The given compound is capable of making both chain isomers and position isomers. But in the structure of formation of product, we have taken only the chain isomers because the options were asked regarding the chain isomers only. These isomers yield differences in the attacking position of a group and so we consider only that.
