Question
Question: complete the reaction: 
Solution
This is a Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement. Here the acid leads to protonation of the hydroxyl group, then removal of water leads to formation of carbocation. Now 1,2-rearrangement occurs leading to formation of a ketone compound.
Complete step by step answer:
-The reaction shown in the question is Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement. This is a method by which 1,2-diols into carbonyl compounds which contain a carbon oxygen double bond. This happens because 1,2-rearrangement takes place under acidic conditions.
A compound which contains 2 hydroxyl groups (-OH) groups, each being attached to a vicinal carbon atom is known as Pinacol.
Pinacolone is the ketone to which the Pinacol is converted after 1,2-rearrangement under acidic conditions.
Hence the reaction is named as Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement.
A basic representation of this reaction can be written as:
(CH3)2(OH)C−C(OH)(CH3)2H+acid(CH3)3COCH3+H2O
-During this reaction the hydroxyl group of the Pinacol is protonated by the acid. Then water is removed which leaves behind a carbocation which is tertiary and hence stable. So, the alkyl group from the adjacent carbon migrates to the carbocation centre which is known as 1,2-rearrangement. Now the oxygen atom which was bonded to the carbon atom via double bond is deprotonated, which gives rise to the Pinacolone.
The reaction will thus proceed as:
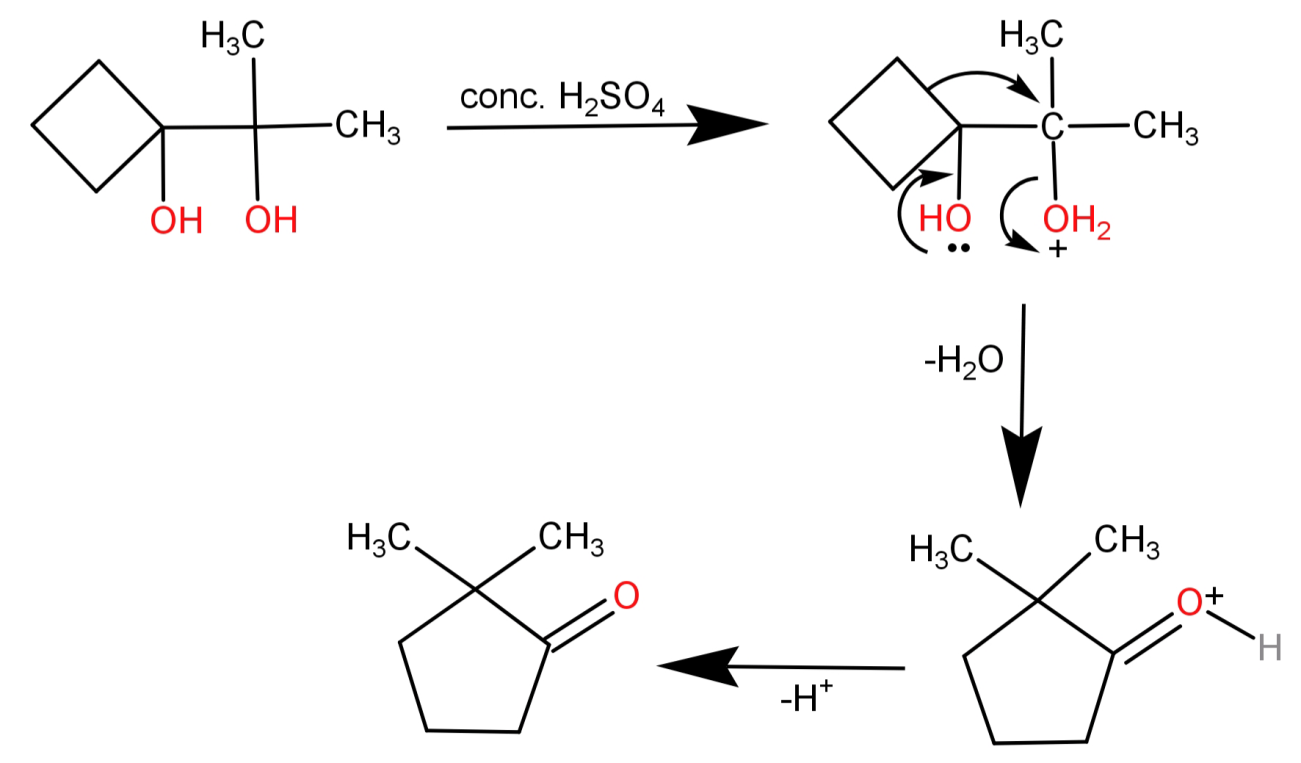
Note: The Pinacol Pinacolone Rearrangement is regioselective in nature, which means that only the more stable carbocation yields a major product. Also the rearrangement occurs because of the relative stability of the resulting oxonium ion.
