Question
Question: Complete the reaction. 
Solution
To answer this question, you should recall the concept of Tishchenko Reaction. This reaction results in the formation of esters using both the corresponding enolizable and non-enolizable aldehydes.
Complete step by step answer:
The most common catalysts used in this reaction are aluminium alkoxides but a wide variety of other catalysts can be used including alkali- and alkali—earth metal oxides and alkoxides, transition metal-based catalysts such as ruthenium complexes and certain rhodium, iridium and iron complexes. The Tishchenko Reaction is a disproportionation reaction that allows the preparation of esters from two equivalents of an aldehyde. Catalysts are aluminium alkoxides or sodium alkoxides. The mechanism of the above reaction can be represented by the following steps:
Step 1: The aluminium alkoxide acts as a Lewis acid to coordinate with one molecule of the aldehyde, and to facilitate the addition of a second equivalent of aldehyde, generating a hemiacetal intermediate:
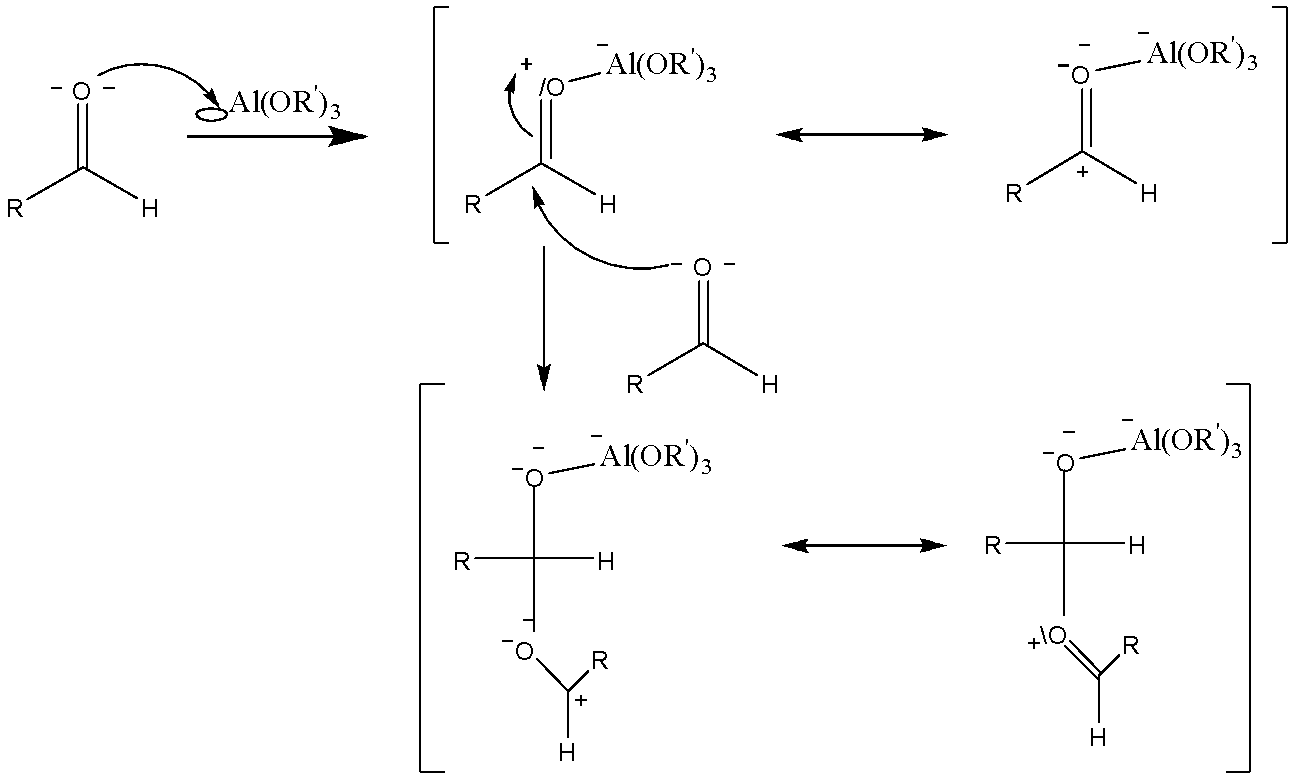
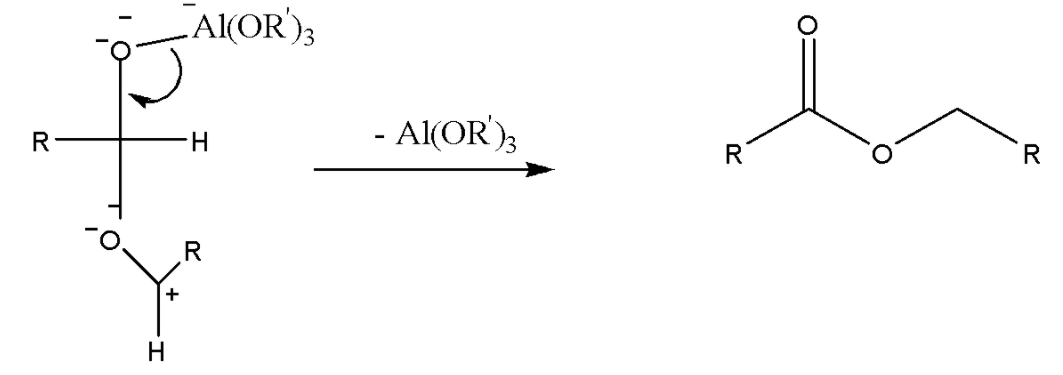
Step 2: This species undergoes an intramolecular 1,3-hydride shift that results in the production of the aluminium-coordinated ester.
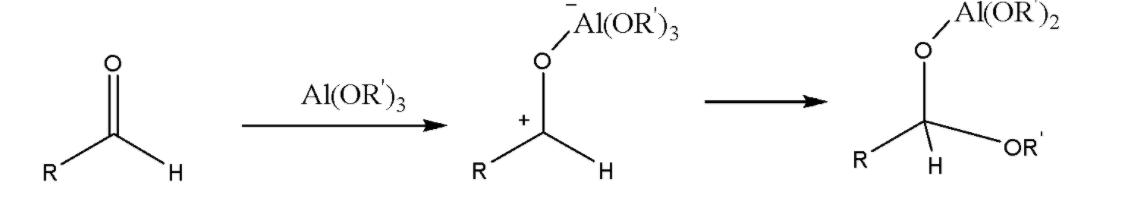
Step 3: A potential side reaction is the involvement of one of the alkoxide groups from the catalyst:
Step 4:
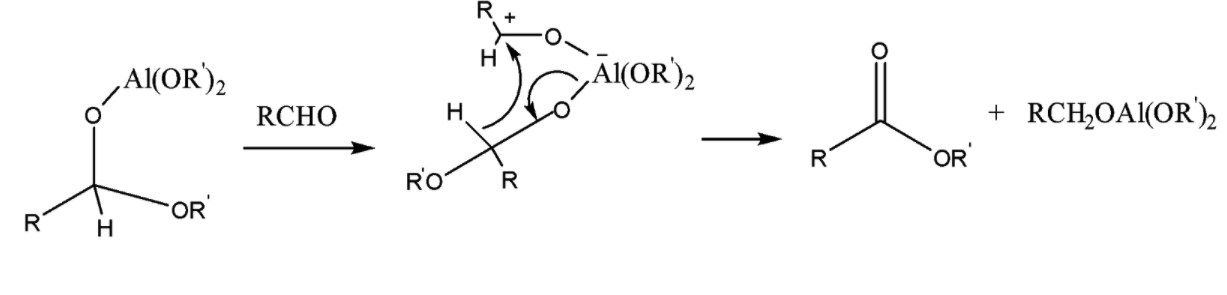
Note:
You should note that in industrial settings the Tishchenko reaction is widely used in industry for the production of simple esters only such as ethyl acetate. Complex esters are often problematic because of the limited scope of the classical Tishchenko and aldol-Tishchenko reactions. However, these reactions can be applied in synthesis with careful choice of a catalyst or promoter compatible with functionality in the starting materials.
