Question
Question: Complete the following reactions: (i) \(C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}N{{H}_{2}}+CHC{{l}_{3}}+alc.KOH\to \) ...
Complete the following reactions:
(i) CH3CH2NH2+CHCl3+alc.KOH→
(ii) C6H5N2+Cl−waterroom temperature
(iii) 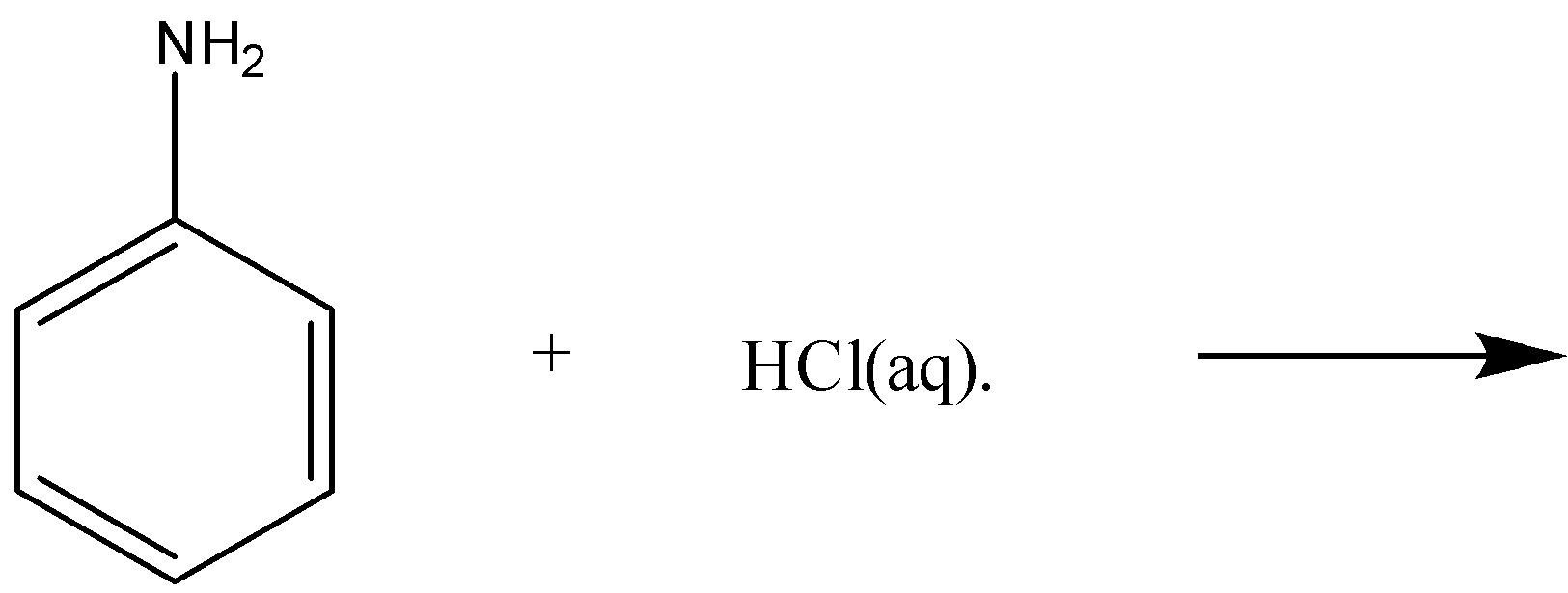
Solution
HHnt: These reactions are based on the concept of nitrogen having positive charge, and the displacement of the group with the other one reactant. In the (i) part reaction is an example of carbylamine reaction. In the (ii) part it is related to the displacement of the nitrogen group. In the (iii) aniline dissolves to form a compound.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, if we talk about the reactions step by step. Let us see the first part (i), as mentioned it is an example of carbylamine reaction. In this reaction primary amines (ethylamine) react with chloroform, and a base i.e. KOH to form the end product isocyanide having by product chloride salt, and water. The complete reaction for part (i) is
CH3CH2NH2 + CHCl3 + alc.KOH → CH3CH2NC + 3KCl + 3H2O
-Now, if we talk about the (ii), here benzenediazonium chloride is unstable, so it further reacts with other molecules, or substances to gain stability. So, we can say benzenediazonium chloride reacts with water at room temperature, and forms phenol, and the by- products nitrogen, and HCl.
The complete reaction for part (ii) is
C6H5N2 +Cl− waterroom temp. C6H5OH + N2 + HCl
-Now, for the part (iii), we have aniline reacting with aqueous HCl, as we know aniline is basic in nature, and HCl is an acid. Here, acid-base reactions will take place. It will lead to the formation of anilinium chloride. The complete reaction for part (iii) is
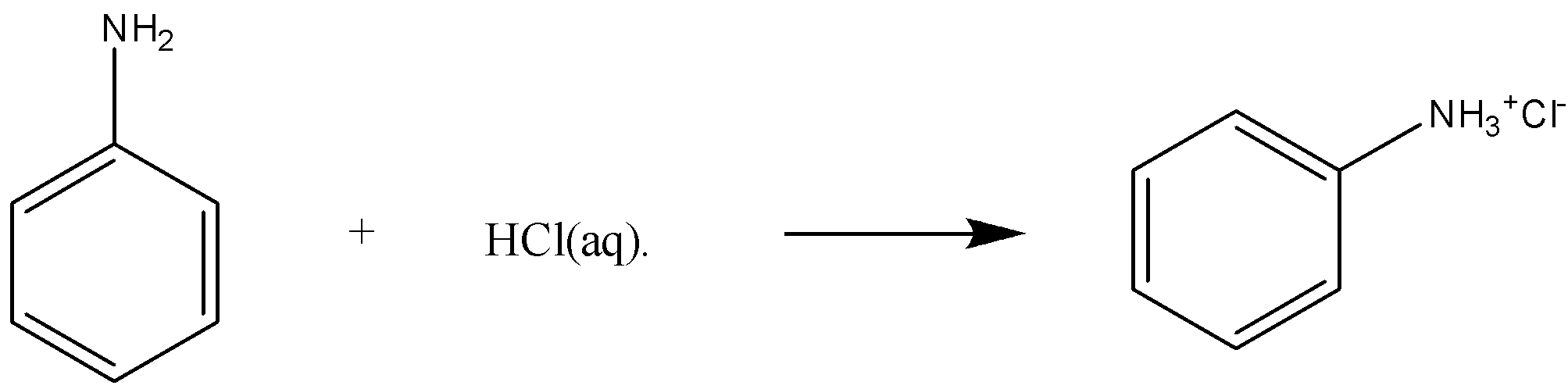
In the last, we can conclude that in part (i), the product ethyl isocyanide, in (ii) a phenol, and in (iii) anilinium chloride.
Note: Don’t get confused while completing the reaction for all three parts. These are different from each other. You must know that carbylamine reaction test is used for primary amines, it doesn’t perform with the secondary, and tertiary amines.
