Question
Question: Complete the following reaction sequence 
Comment on the acidic nature of B.
Solution
Internal alkynes are reduced to trans-alkenes with NH3Li. Alkenes are less acidic than alkynes because of its sp2 hybridized carbon atoms. The order of acidity is single bond < double bond< triple bond. The treatment of alkenes with hydrobromic acid (HBr) will result in the formation of alkyl bromides.
Complete step by step answer:
Lithium in liquid ammonia or sodium in liquid ammonia are good reducing solvents and these solvents are used to reduce Alkynes to Alkenes. Alkynes can be reduced to trans-alkenes with the use of lithium dissolved in an ammonia solvent. An Li radical donates an electron to one of the π bonds in a carbon-carbon triple bond. This forms an anion, which can be protonated by a hydrogen in an ammonia solvent. This prompts another Li radical to donate an electron to the second π orbital. Soon after this anion is also protonated by a hydrogen from the ammonia solvent, resulting in a trans-alkene.
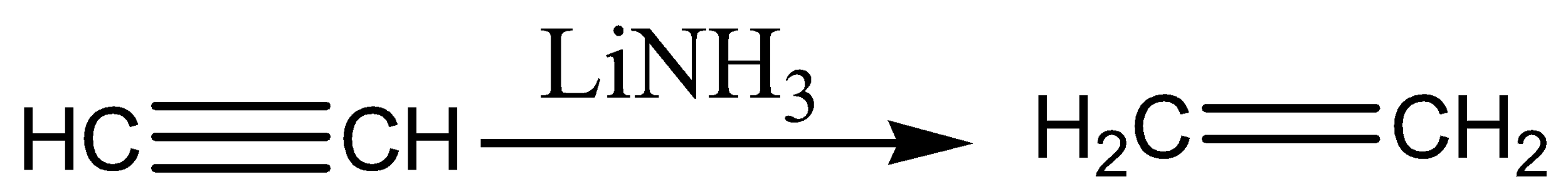
In the above reaction, internal alkynes are reduced to trans-alkenes with NH3Li. Hence, Acetylene is reduced to ethene (A). Ethene on treatment with ethyl chloride gives 1-butene (B) which on treatment with HBr form bromine radicals by abstracting hydrogen from hydrogen bromide and this step is an exothermic reaction that gives 1-bromobutane (C).
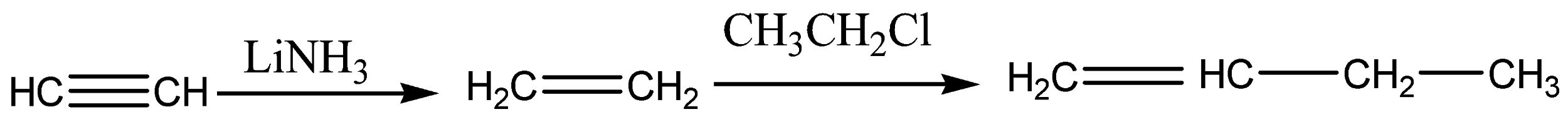
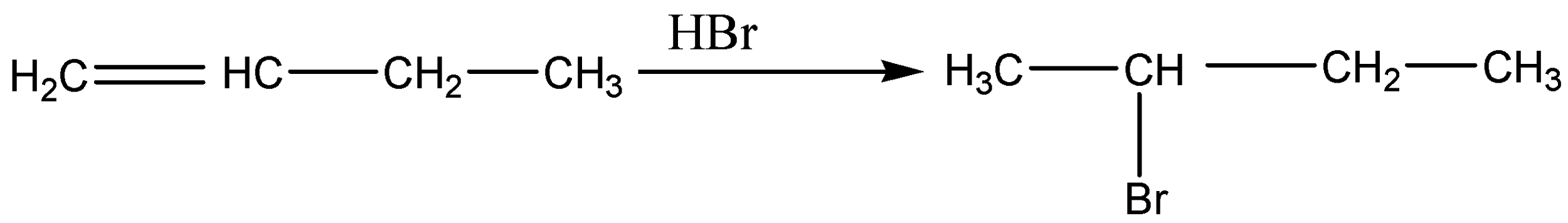
The acidic nature of B is that it is mildly acidic because it has sp2 hybridized carbon atoms.
Note: The acidity of alkynes is always greater than the acidity of alkanes and alkenes as the carbon atom in alkanes and alkenes are sp3 and sp2 hybridized respectively. So, these molecules have a smaller percentage of ‘s’ character in comparison to alkynes. Thus, the electronegativity of carbon atoms in alkanes and alkenes is lesser than that of alkynes. Hence, alkanes and alkenes don’t show the reactions with bases to liberate hydrogen gas.
