Question
Question: Complete the following ray diagram 
Solution
Use the thin lens formula to find the image distance. Use the rules of refraction through the lens to construct the ray diagram.
Formula used: v1−u1=f1
Here
v is image distance
u is object distance
f is focal length of lens
Complete step by step solution:
As shown in the figure
f=+Fu=−23F
Substituting in the given formula
v1=u1+f1v1=−32F1+F1v1=31F1v=3F
Therefore, the image will be formed on the opposite side of the lens as that of the object.
Magnification is
m=uv=−2
Therefore, the image will be inverted and twice the size of the object.
The ray diagram can be constructed using the following rules
1. A ray passing parallel to the principal axis will pass through the focus after refraction.
2. A ray passing through the focus will pass parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
A real, inverted and magnified image will be formed as shown below
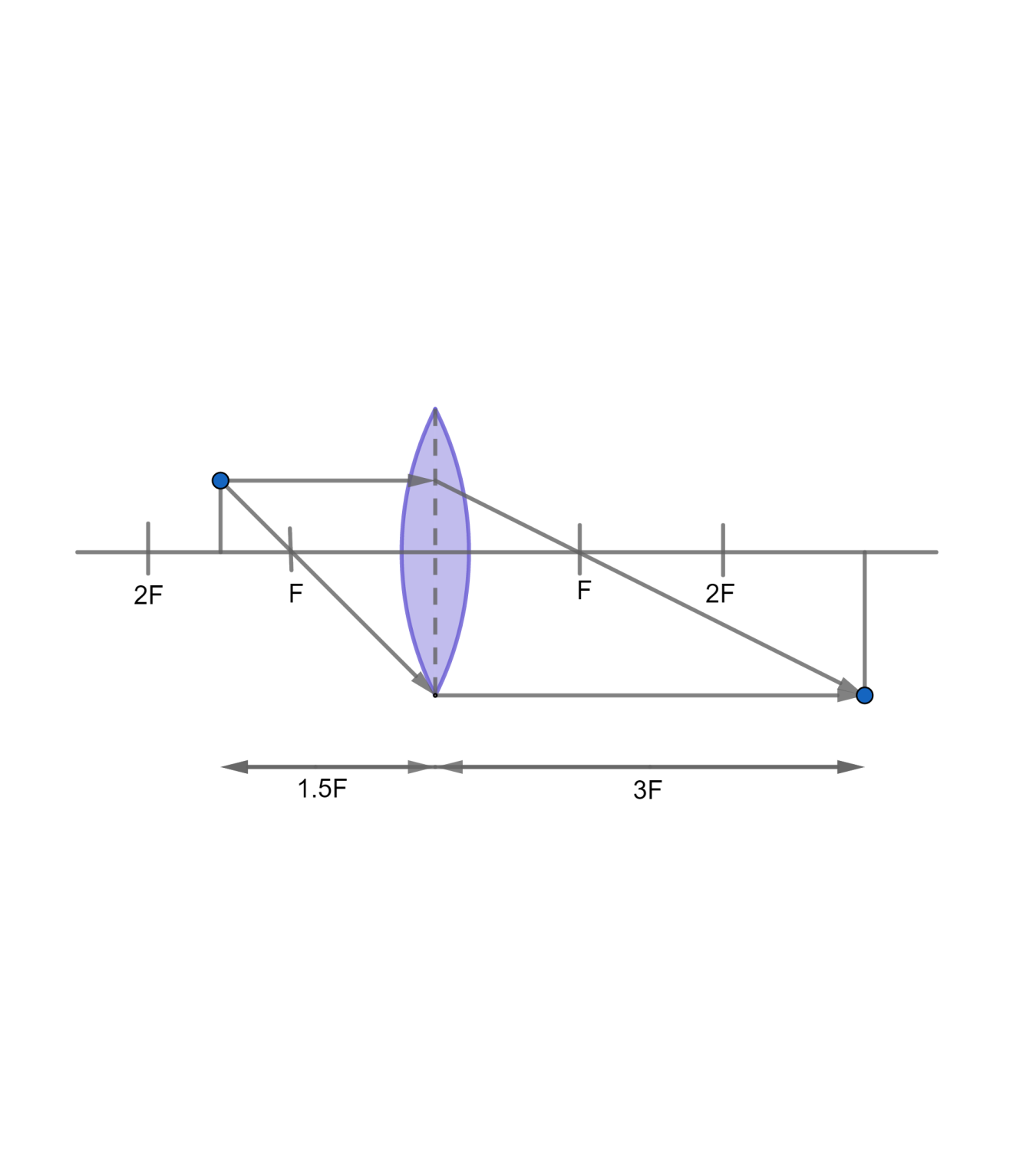
Note: A convex lens produces a real image when the object is farther than the focus and a virtual image when the object is nearer than the focus. A concave lens always produces a virtual image.
