Question
Question: Compare the areas under the curves \(y={{\cos }^{2}}x\ and\ y={{\sin }^{2}}x\) between \[x=0\ and\ x...
Compare the areas under the curves y=cos2x and y=sin2x between x=0 and x=π.
Explanation
Solution
Hint: We will first start by drawing the rough sketch of the graph of both y=cos2x and y=sin2x. Then we will find the area between x=0 and x=π and then compare the result.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we will first draw the graph of y=sin2x and y=cos2x,
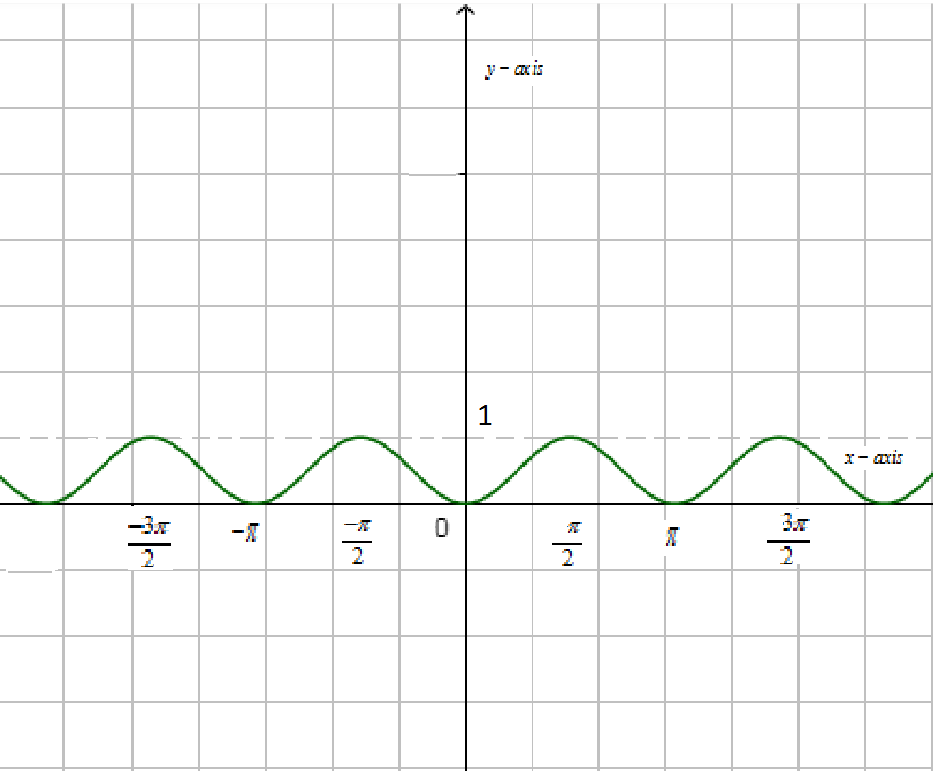
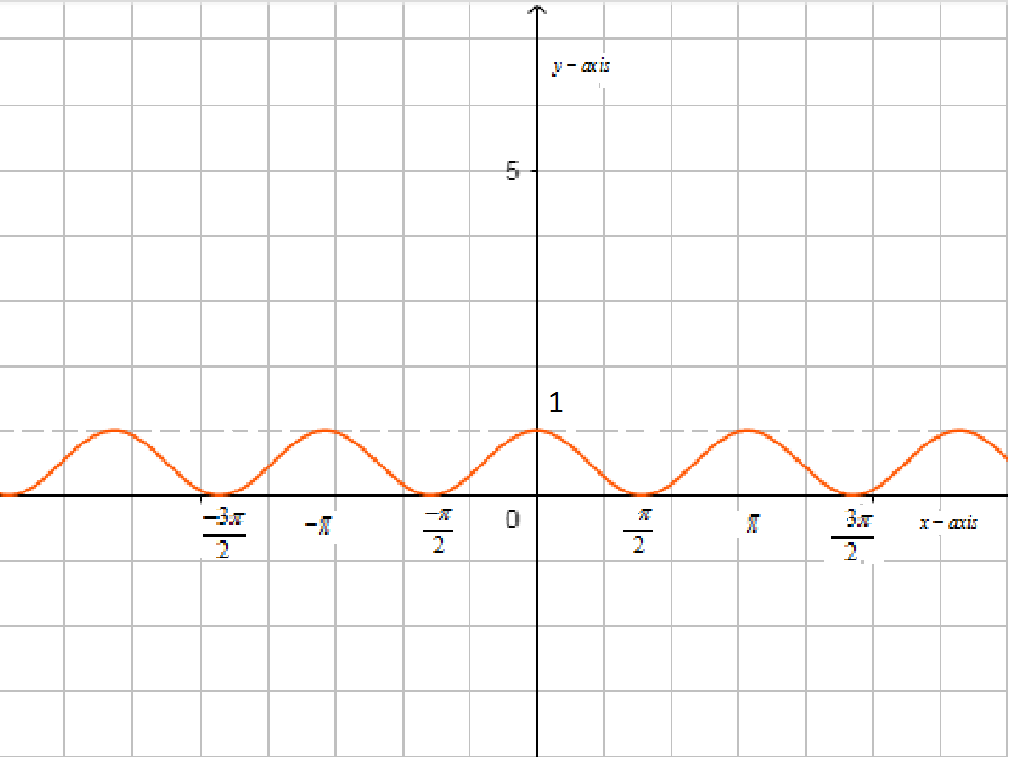
Now, we have to find the area of sin2x between 0 to π. We know that the area under the curve is ∫f(x)dx.
⇒0∫πsin2xdx
Now, we know the trigonometric identity that,
cos2x=1−2sin2x⇒1−cos2x=2sin2x⇒sin2x=21−cos2x
Now, using this in integral we have,
