Question
Question: Compare C4 and C3 pathways of CO2 fixation during photosynthesis. Give a well labelled schematic ske...
Compare C4 and C3 pathways of CO2 fixation during photosynthesis. Give a well labelled schematic sketch of the C4 pathway.
Solution
In photosynthesis, plants and other natural mixes utilize the energy from daylight to extricate supplements from air and water. Photosynthetic creatures highlight a green compound known as chlorophyll that contains the proteins ATP and NADPH. With the energy assimilated from daylight, photosynthetic mixes convert these catalysts to ADP and NADP+.
Complete answer:
The C3 network displays a thicker geography structure than C4. The reproduction of chemical knockouts showed that both C3 and C4 networks are hearty, particularly while improving CO2 obsession. Besides, the C4 plant has better vigor regardless of the target work is biomass combination or CO2 obsession.
Moreover, all the fundamental responses in the C3 network are likewise basic for C4, while there are some different responses explicitly basic for C4, which approved that the essential digestion of C4 plants is like C3, however, C4 is more unpredictable.
It likewise distinguished more associated response sets in C4 and showed C4 plants have better-measured quality with complex components that arrange the responses and pathways than that of C3 plants. The expansion of both biomass creation and CO2 obsession with light force and CO2 focus in C4 is quicker than that in C3, which reflected more effective utilization of light and CO2 in the C4 plant.
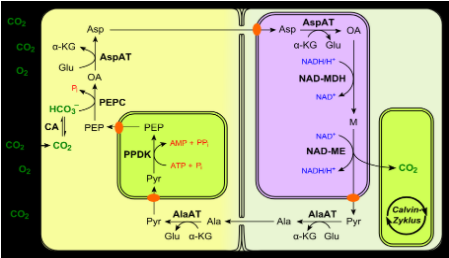
Note: In C4 photosynthesis, where a four-carbon compound is delivered, extraordinary leaf life systems permit carbon dioxide to gather in 'group sheath' cells around Rubisco. C3 plants don't have the anatomic structure (no group sheath cells) nor the bounty of PEP carboxylase to dodge photorespiration like C4 plants. In hot and dry conditions C4 photosynthesis is more productive than C3 photosynthesis. This is because the framework does not go through photorespiration, a cycle that opposes photosynthesis.
