Question
Question: Comment on the structure of liquid \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{6}}}\)....
Comment on the structure of liquid I2Cl6.
Solution
Iodine and chlorine both belong to the same group i.e. halogen group. I2Cl6is formed by two molecules of ICl3. This is a complex compound formed by ICl3. The two chlorine atoms of I2Cl6are linking atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
Covalent bond: Those bonds between the atoms in which both the atoms share the electrons to each other.
Coordinate covalent bond: The bond in which the electron is donated by one atom but shared by both the atoms.
I2Cl6is formed by two molecules of iodine trichloride. Iodine trichloride is the interhalogen of iodine with chlorine. Here iodine is at centre because its size is large as compared to the size of chlorine. In the structure of I2Cl6two chlorine atoms are linking atoms. Linking atoms are those atoms which are linked to two atoms one by covalent bond and other by the bond in which the electron is donated by one atom but shared by both the atoms i.e. coordinate covalent bond. So they have different angles between the iodine- chlorine atoms. Because all the chlorine atoms present in the I2Cl6molecule is not the same. So they have different bond lengths and angles.
The structure of the I2Cl6molecule is as follows:
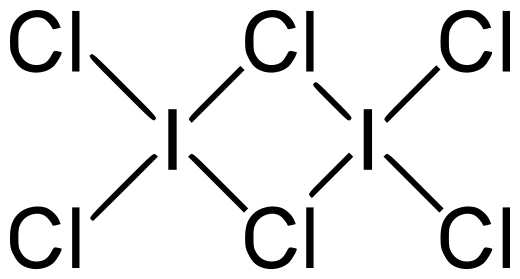
In this structure the chlorine are of two types: the one which is connected to only one iodine atom and the second one is that which is connected to two iodine atoms.
Note:
The structure can be studied by using molecular orbital theory (M.O.T). It can be defined as how electrons or atoms are assigned in the molecule. Although electrons are not moving there but they are treated as moving under the influence of atomic nuclei in the whole molecule.
