Question
Question: Classify the following compounds based in the pattern of carbon chain and give their structural form...
Classify the following compounds based in the pattern of carbon chain and give their structural formula:
a. Propane
b. benzene
c. cyclobutane
d. furan
Solution
. When a compound has the suffix- ane , it means it is an alkane, for-ene the compound is an alkene, means it has at least one double bond. Prefix like cyclo indicates that the compound is cyclic in structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us find out the structural formulas of the following organic compounds:
Propane: Propane is an organic compound that has 3 carbon atoms and is an alkene with a straight chain. 3 carbon atoms are due to the prefix ‘prop’. It has a chemical formula C3H8 and is a paraffin hydrocarbon. There is no unsaturation present. The structural formula of propane is:
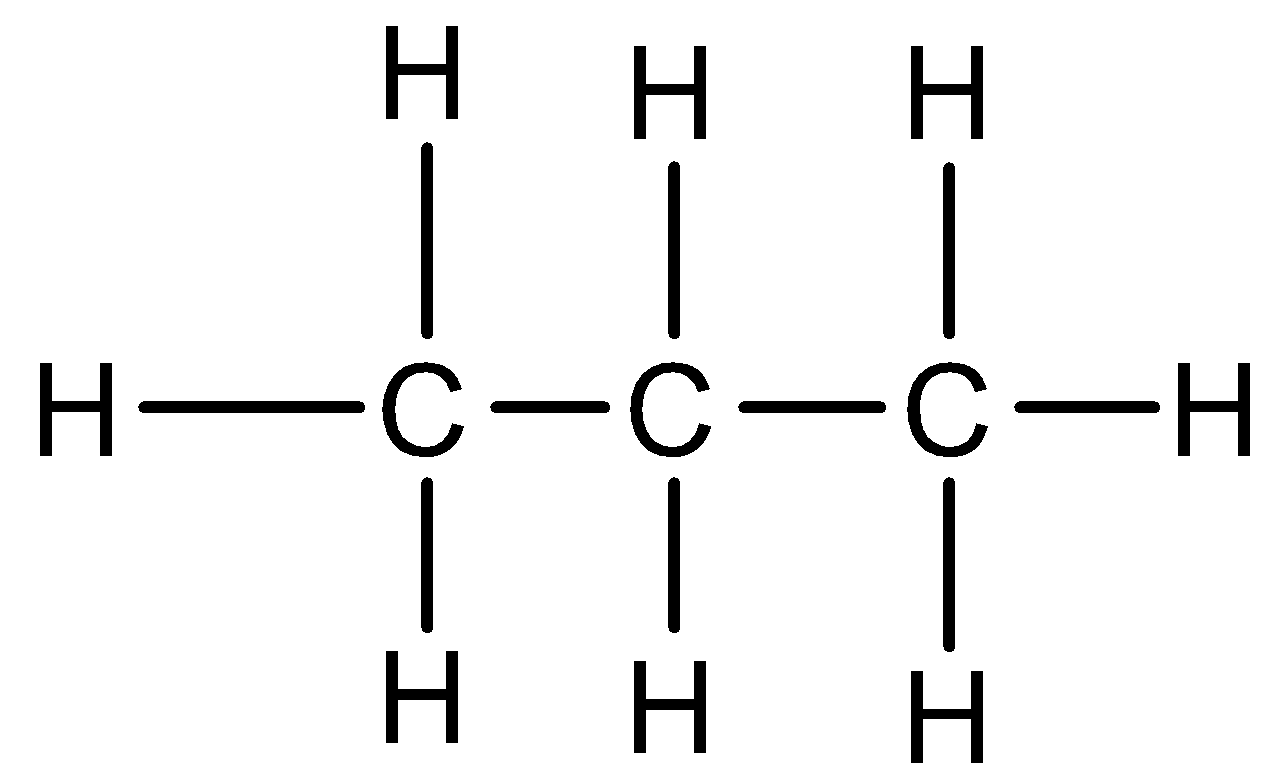
Benzene: Benzene is an organic compound that has 6 carbon atoms and is cyclic in nature. Moreover, the bonds in benzene are alternatively single and double bonded. It has a chemical formula C6H6 and benzene is also an aromatic compound. The structure of benzene look like this:
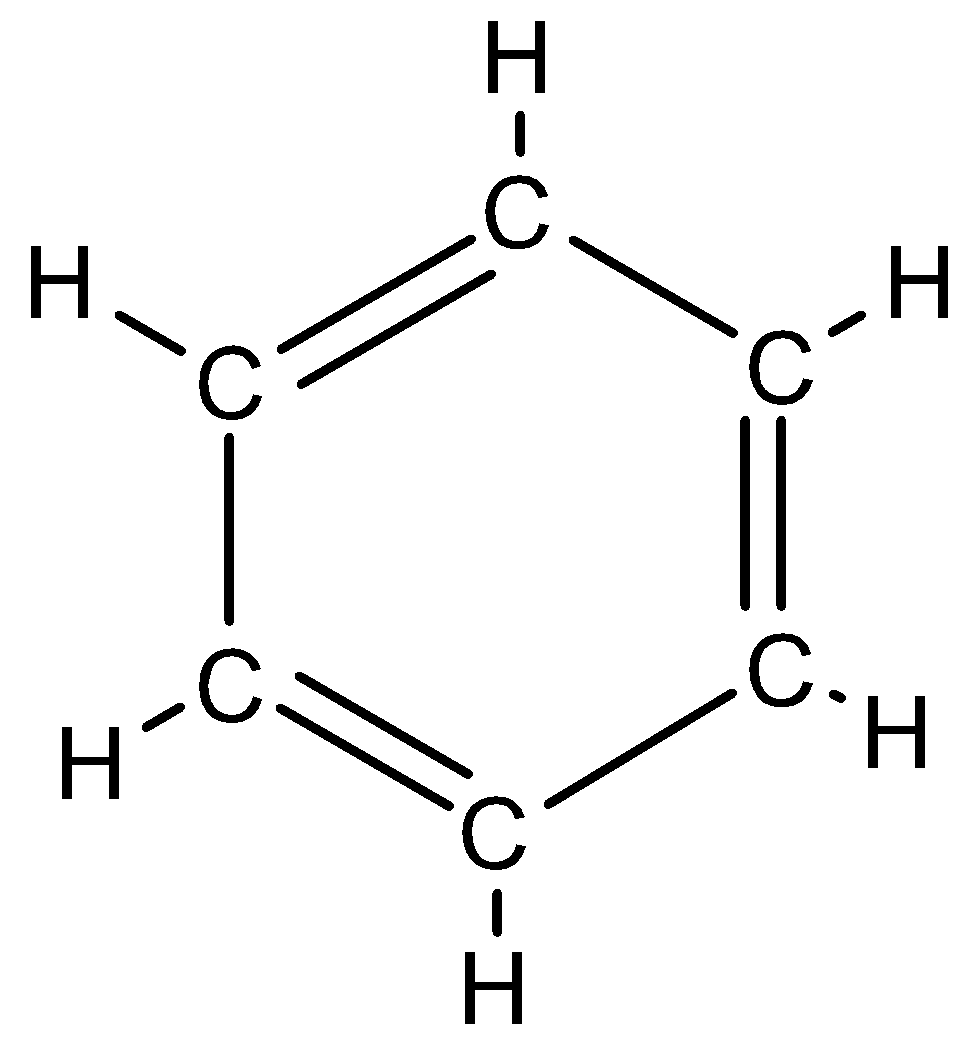
Cyclobutane: In the compound cyclobutene, the number of carbon present is 4 and there is no double or triple bond present. However, it has a cyclic structure and has the chemical formula of C4H8. It is a colourless gas which is often used as a fuel by liquefying it. The structure of cyclobutene is:
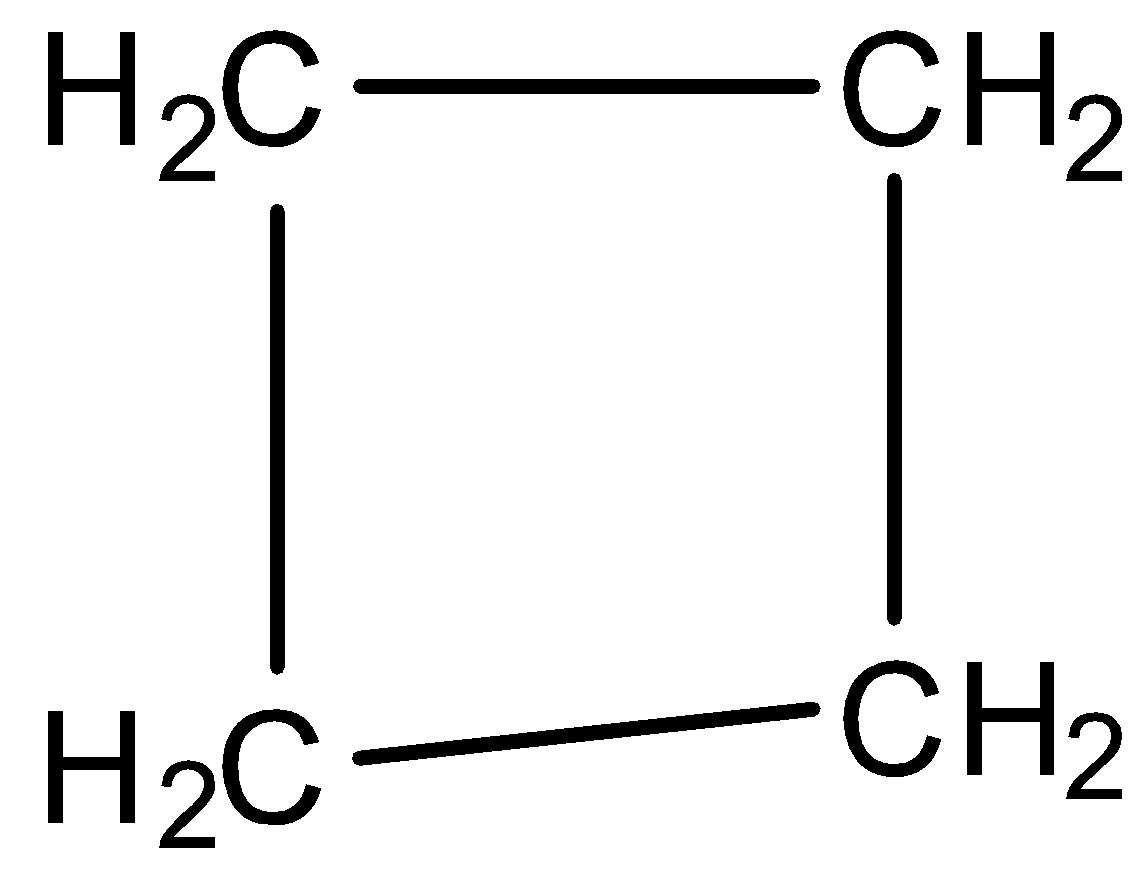
Furan: Furan is an organic compound that is heterocyclic in nature. That means, it has atoms other than carbon and hydrogen present. It is a five membered ring that has four carbon atoms and one oxygen. It has the chemical formula C4H4O. The structure of furan appears as:
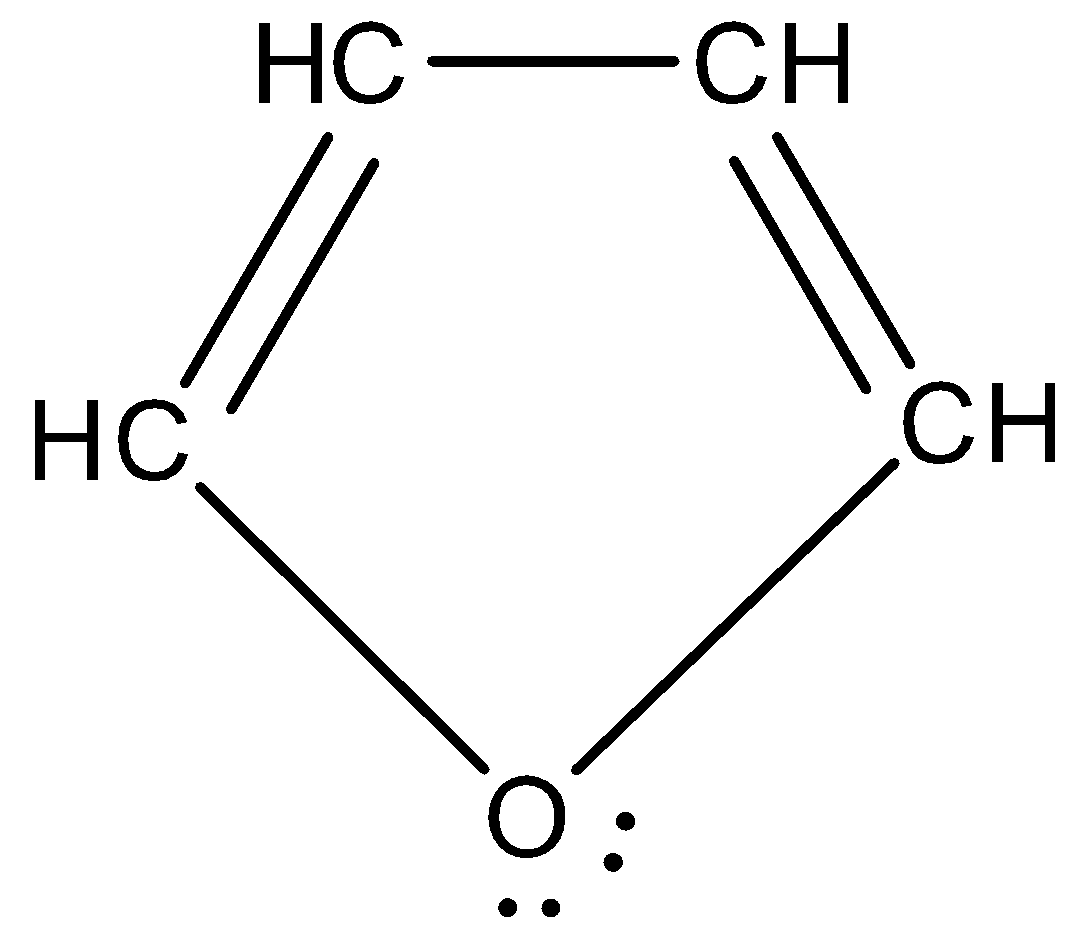
Note: It is to be noted that for the same chemical formula, the compound may have different structures. For example cyclobutane and butene have the same chemical formula, but their structures are different. Such structures are called isomers.
