Question
Question: \(Cis - 2 - butene\) on reaction with bromine in carbon tetrachloride produces mainly. A) \(1 - br...
Cis−2−butene on reaction with bromine in carbon tetrachloride produces mainly.
A) 1−bromo−2−butene
B) 2,3 - dibromobutane
C) meso - 2,3 - dibromobutane
D) +−2,3−dibromobutane
Solution
We know that,
The addition of bromine to the Cis−2−butene is clearly determined by the anti-addition and the almost completely restricted rotation of the carbon-carbon double bond of the halonium ion. Therefore, the bromination of Cis−2−butene on gives a racemic mixture of (2R, 3R) - and (2S, 3S)-dibromobutane, whereas the bromination of trans−2−butene on gives the meso compound.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the cis and trans isomers are geometrical isomers. Let us discuss the geometric isomer.
Geometric isomers:
Geometric isomers are isomers which arise due to different arrangements of atoms or groups around a bond which has restricted rotation. Geometric isomers are also known as Cis- trans isomerism.
-If the two atoms are locked on the same side of the molecule then it is called cis isomers.
-If the two atoms are locked on the opposite side of the molecule then it is called trans-isomers.
First we see the structure of Cis−2−butene
The addition of bromine to Cis−butene on produces an achiral bromonium ion intermediate. Consequent attack of the bromide ion gives the same product because the bromonium ion is symmetrically substituted. The product of the reaction is the racemic mixture of the enantiomeric product (2R,3R) - 2,3 - dibromobutaneand (2S,3S) - 2,3 - dibromobutane.
The reaction is can be written as,
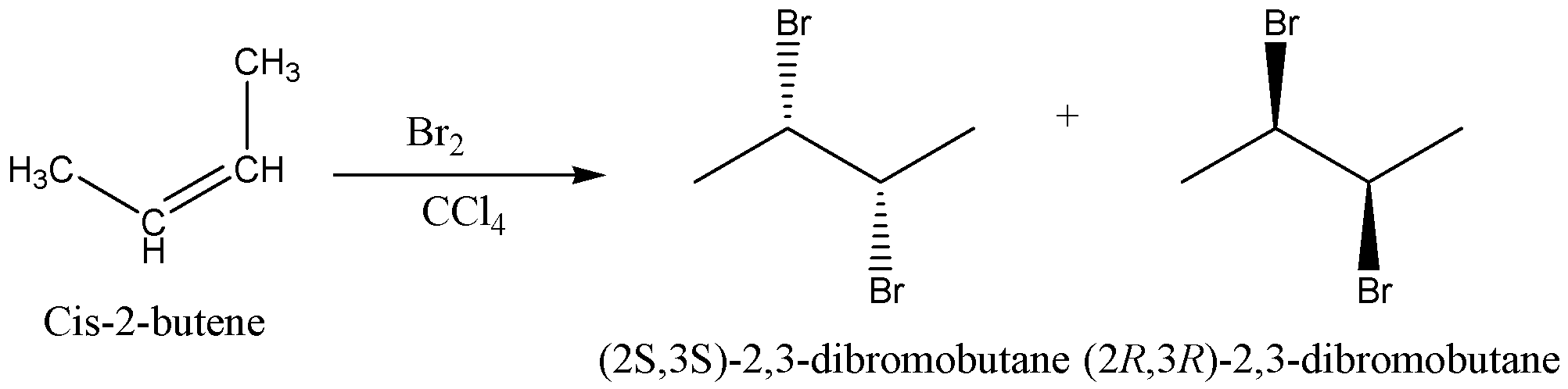
Therefore, the option D is correct.
Note:
On the other hand, a chiral intermediate bromonium ion is formed by the addition of bromine to the trans isomer. The products are meso compounds (2S,3R) - 2,3 - dibromobutaneand (2R,3S) - 2,3 - dibromobutane and therefore they are identical.
