Question
Question: Chromosome duplication without nuclear division refers to (a) Meiosis (b) Mitosis (c) Androge...
Chromosome duplication without nuclear division refers to
(a) Meiosis
(b) Mitosis
(c) Androgenesis
(d) Endomitosis
Solution
This is often found in insects and tissues of some vertebrates, which form cells with a polyploid nucleus. Polytene chromosomes (huge chromosomes) are also formed as a result of this process.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
Endomitosis is the process of chromosome divides or doubles without nuclear division which leads to the formation of a polyploidy nucleus where one nucleus will have multiple sets of chromosomes.
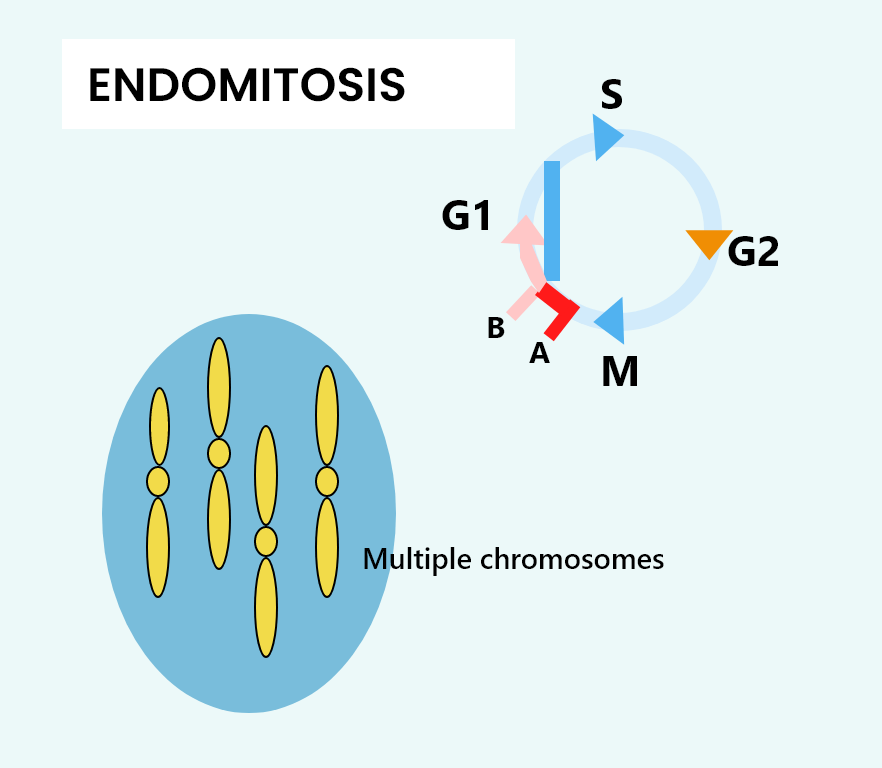
So, the correct answer is ‘Endomitosis’.
Additional Information:
- In- plant cells endomitosis is commonly found in tapetum where the nuclear membrane does not disappear, but the chromosomes are condensed more than that of normal mitosis during the metaphase.
Meiosis: A process where a single cell produces four daughter cells by replicating twice, where each cell contains half of the original amount of genetic material from the parent cell.
- Gametes (sex cells – egg in females and sperm in males) are produced by meiosis. The process of meiosis is divided into two major stages known as meiosis I and meiosis II.
Mitosis: A process where a single parent cell divides or replicates into two identical daughter cells, which is commonly known as cell replication or binary division.
- Mitosis occurs in our normal cells by which the cells increase their number and also replaces dead cells.
- Mitosis is divided into 5 stages, which are Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Androgenesis: The process of formation of embryos without the genetic material from oocytes.
- In androgenesis, there is no participation by the female reproductive cell in the process of reproduction.
Note:
- In mitosis, the daughter cells are genetically identical, wherein meiosis the daughter cells are not genetically identical and result in the formation of haploid daughter cells.
- Diploid cells have two sets of chromosomes in which one set is obtained from each parent, where haploid cells have just a single copy of each chromosome.
