Question
Question: Choose the correct option(s) that give(s) an aromatic compound as the major product: A.  that give(s) an aromatic compound as the major product:
A. 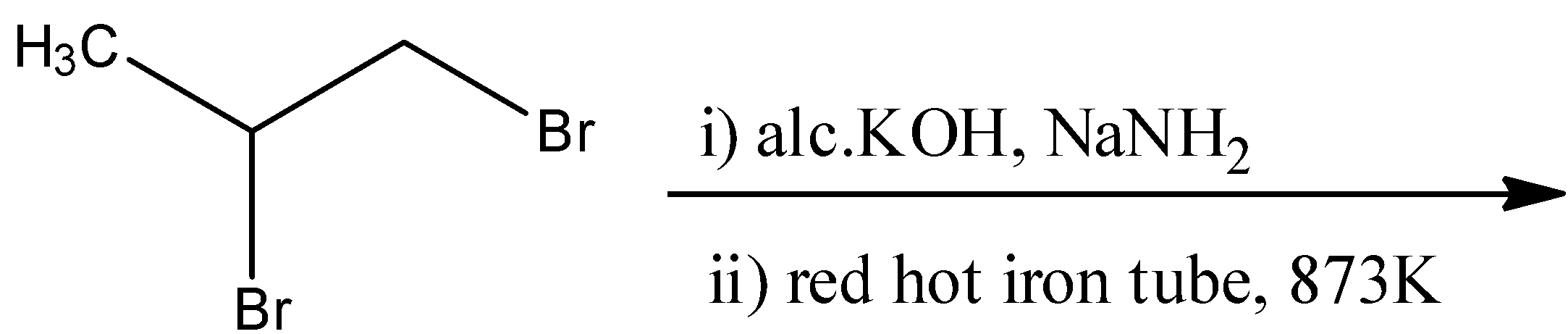
B. 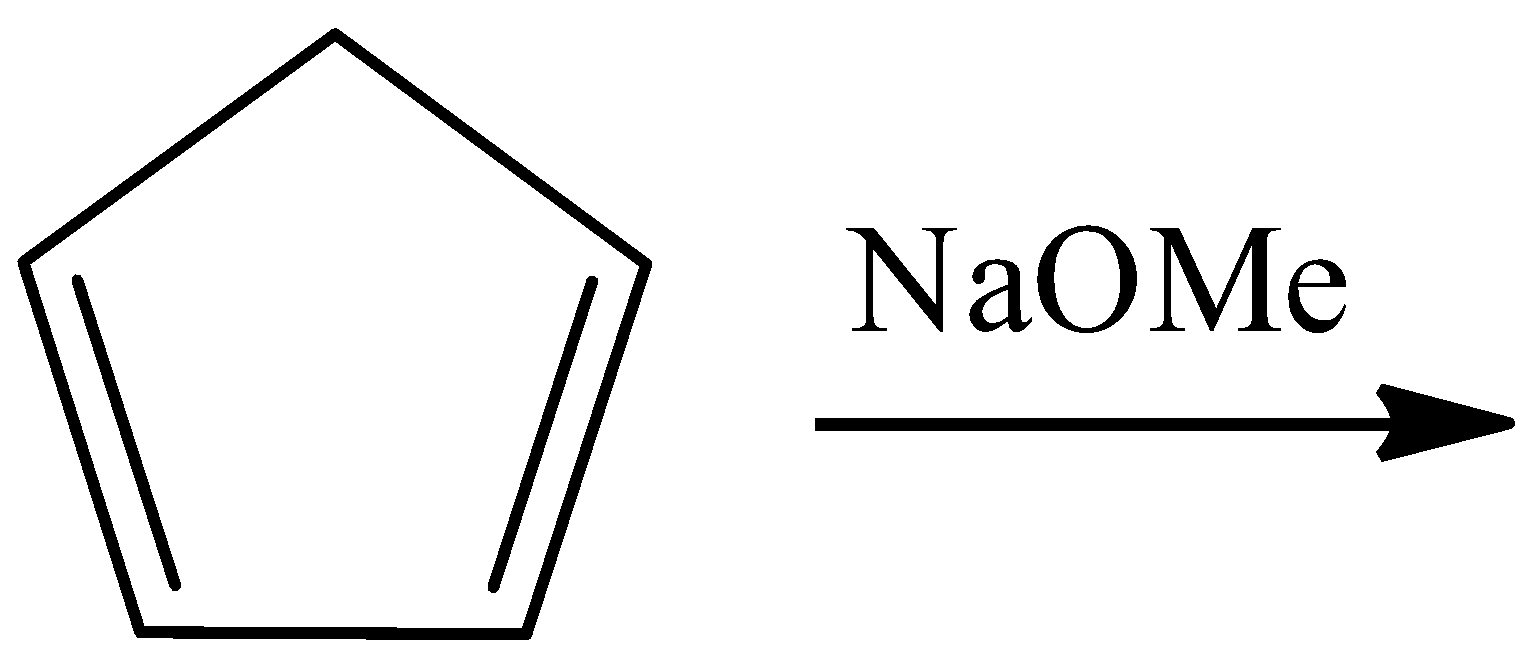
C. 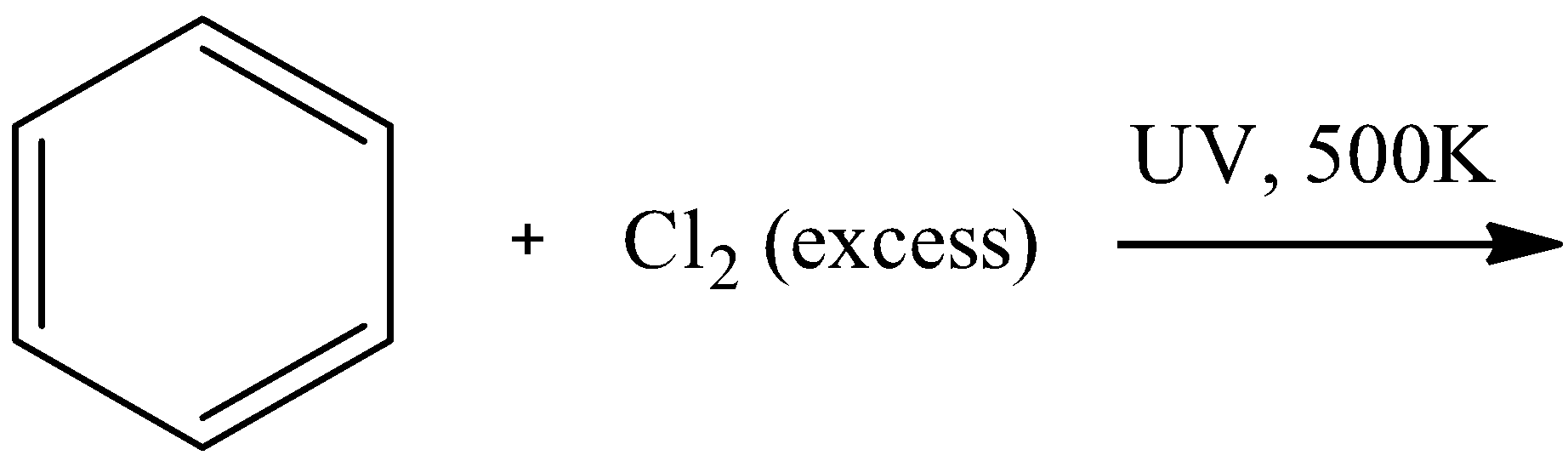
This question has multiple correct options
Solution
Predict the products of the reactions given in the options and check if the major product adheres to the rule that defines all aromatic compounds. This rule pertains to the number of pi-bonding electrons that are present in the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that general rule that is used to determine whether a cyclic molecule is considered to be aromatic or not. Of all the electrons, the number of pi-electrons should be equal to 4n+2, where n is any natural number. So, the number of pi-electrons can be 6, 10, 14, etc. Now we will look at each of the reactions one by one and check if the products are aromatic or not.
- For option A
The geminal dihalide that is given in the reaction will undergo dehydrohalogenation two times to form an alkyne. The reactant will react with alcoholic KOH in the presence of sodium amide in liquid ammonia to form a propyne molecule. This propyne molecule will then undergo cyclization in a red-hot iron tube to form hexamethylbenzene. The reaction for this is as follows:
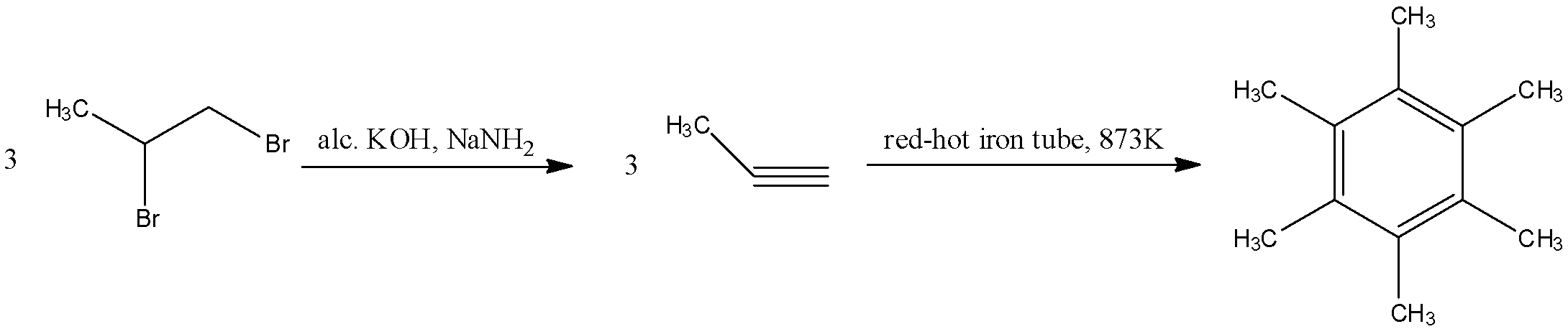
Here, the number of pi-electrons are 6, which fits into our formula of 4n+2. Hence, this is an aromatic compound.
- For option B
In this reaction, pentene reacts with sodium methoxide to give an ionic species that has a negative charge on the only sp3 hybridized carbon atom in the reactant. This makes that atom partially sp2 hybridized and planar. The reaction is as follows:
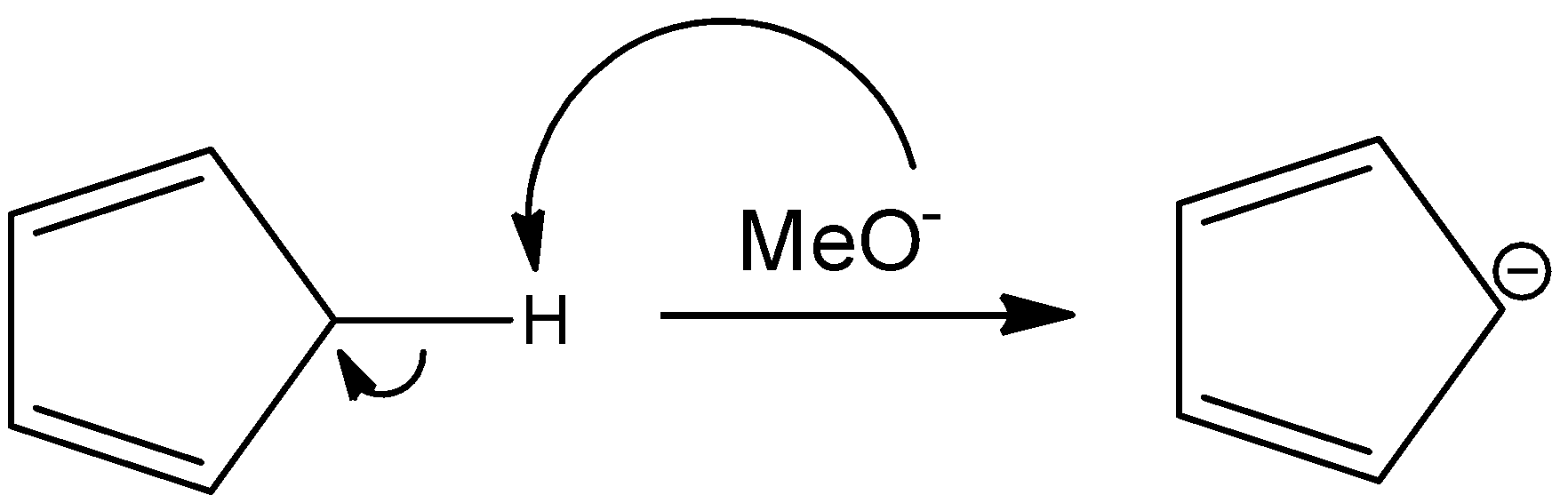
Here again, the number of pi-electrons are 6, the negative charge that is present on the ring will form a pi-bond with any components within the ring and will contribute to the resonating structures of the ring as pi-electrons. Hence, this is also an aromatic compound.
- For option C
We know that the bond between the Cl atoms breaks in ultraviolet light and the formation of free radicals takes place. These free radicals can easily break the double bonds in the benzene ring and cause its halogenation on all the 6 sites possible to form hexachlorocyclohexane. The reaction is as follows:
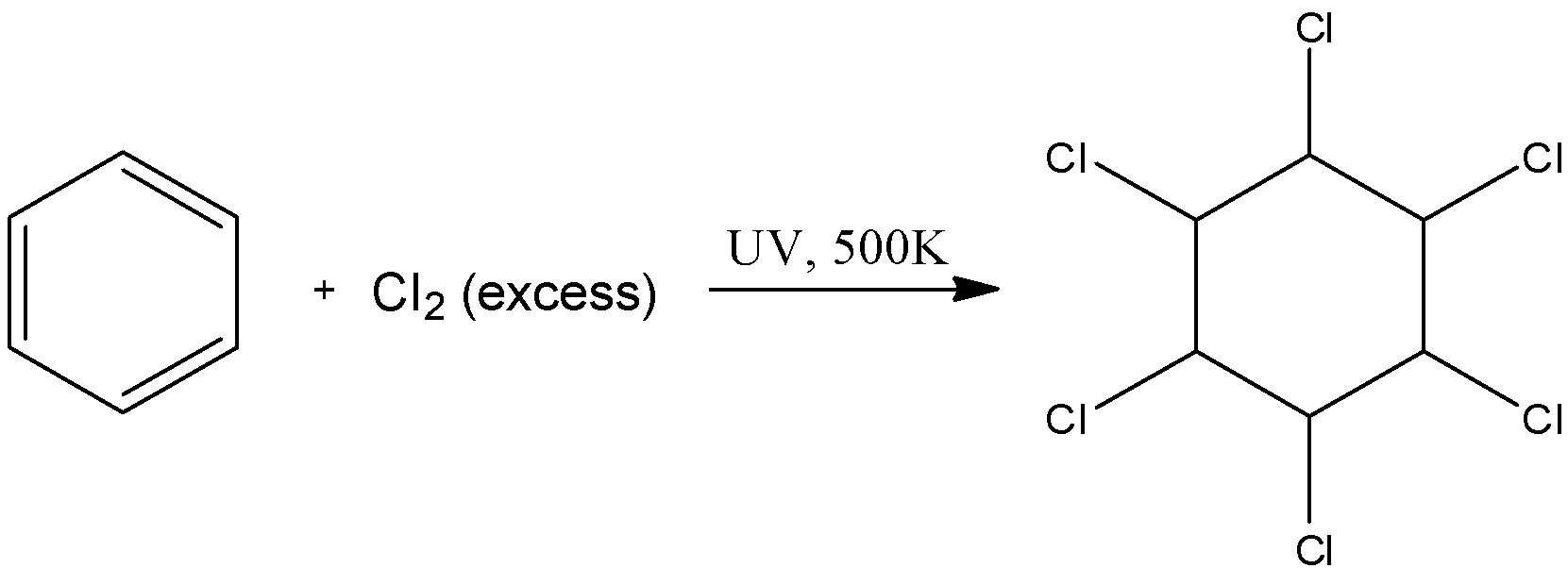
Here, we can see that there are no pi-electrons present. Thus, this is not an aromatic compound.
From the above set of reactions, we can identify that the reactions giving aromatic compounds as major products are options (B) and (C). So the correct answer is “B and C”:
Note: Remember that for a cyclic compound to be aromatic, the presence of double and single bonds in an alternating manner is also necessary. If the molecule satisfies the rule for the pi-electrons then check if the bonds are alternating in nature, if they are not, then the compound is not aromatic.
