Question
Question: Choose the correct answer among the alternatives given: Bromination of methane in presence of sunlig...
Choose the correct answer among the alternatives given: Bromination of methane in presence of sunlight is a:
A. nucleophilic substitution
B. free radical substitution
C. electrophilic substitution
D. nucleophilic addition
Solution
The chemical reactions proceed with bond-making and some with bond-breaking. When two bonds break, energy is absorbed to separate their molecules but when two bonds are formed, energy is released as the molecules come closer.
Complete step by step answer:
In a chemical reaction, the bond breaking and bond making can happen in two ways. One is homolytic and the other one is heterolytic. In a homolytic equal division of electrons happens and radical is formed. On the other hand, in heterolytic unequal cleavage of bonding is happened. And cation and anion are formed.
By the Law of Conservation of Energy, we know that the total energy of a system must remain unchanged, and that is why a chemical reaction tends to absorb or release energy in the form of heat, light, or both.
Practically any reactions at heat undergo heterolytic cleavage and cation and the anion is formed. On the other hand, any reaction in presence of radiation of light like sunlight, the homolytic cleavage happens.
Therefore, when the reaction in the bromination of methane in presence of sunlight, homolytic cleavage happens and radical is formed. By radical formation bromine radical substitute, the hydrogen atom from methane. As here substitution reaction is happening by the formation of radicals, this overall reaction is called free radical substitution. The reaction is as follows,
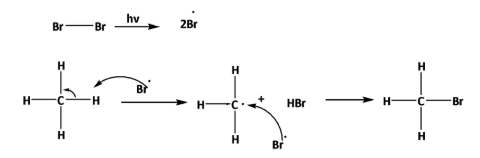
So, the correct option is B.
Note:
The change of energy in a chemical reaction is because of the difference in the amounts of stored chemical energy between the products and the reactants. Due to the absorption of energy when chemical bonds are broken and the release of energy when chemical bonds are formed. An exothermic reaction is said to have a negative enthalpy of reaction. This means that the energy required to break the bonds in the reactants is less than the energy released when new bonds are formed in the products. And therefore, excess energy from the reaction is released as heat and light.
