Question
Question: Chlorobenzene reacts with trichloro acetaldehyde in the presence of \({{H}_{2}}S{{O}_{4}}\). The maj...
Chlorobenzene reacts with trichloro acetaldehyde in the presence of H2SO4. The major product formed is:
A.
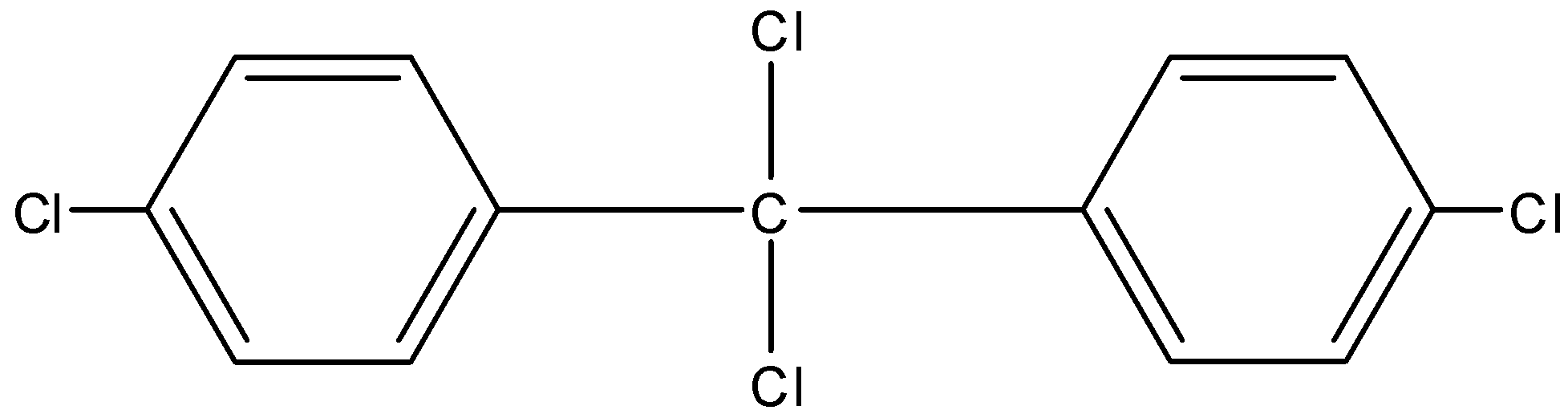
B.
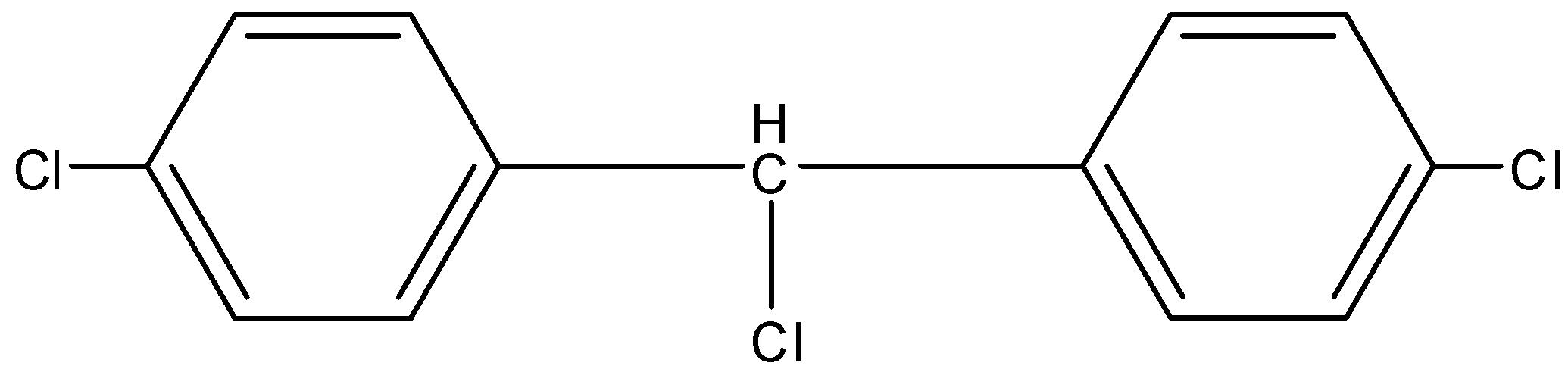
C.
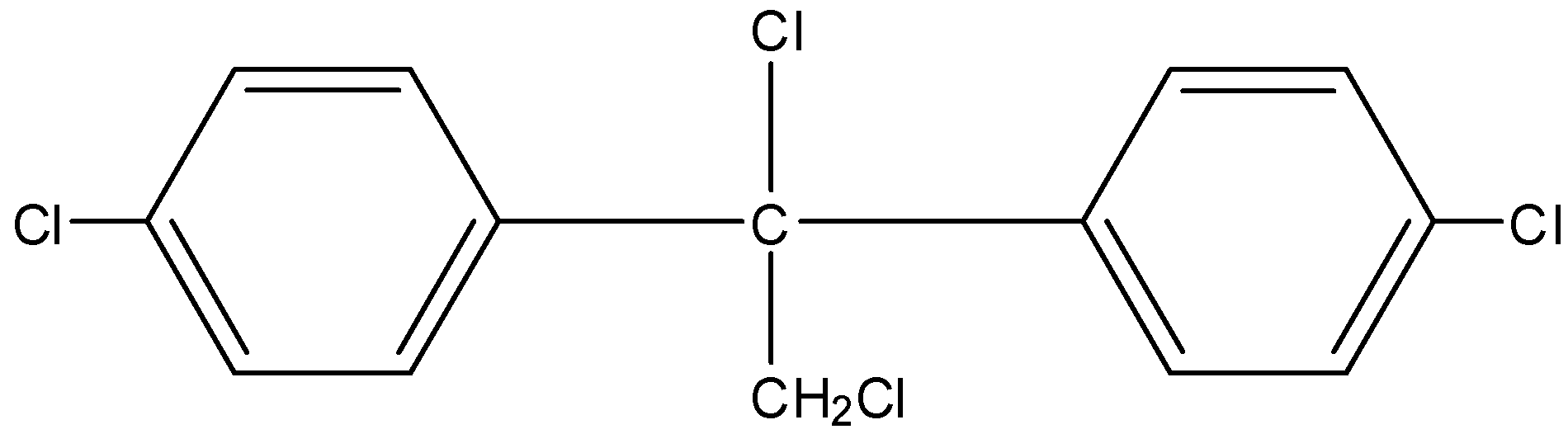
D.
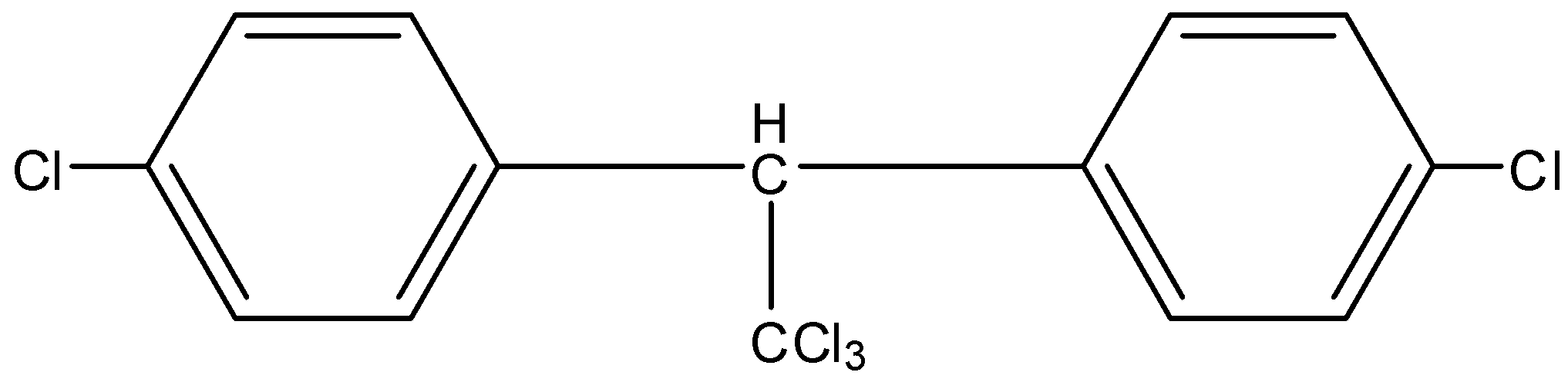
Solution
When Chlorobenzene reacts with trichloroacetaldehyde in the presence of H2SO4, there product so formed is a powerful insecticide and is used in many places.
Complete Solution :
- In the question, we have the reactants chlorobenzene and an aldehyde. In presence of a strong acid, H2SO4, the oxygen atom on the aldehyde undergoes protonation, thereby forms a carbocation intermediate. Since a carbocation is formed, there is an electrophilic attack on the phenol, in the para position. Chlorobenzene has -I and +M effect. Since it is +M, it has some directing effects on the para position as well. A minor product is formed.
- Since H2SO4 is a very strong acid, it will protonate the OH group further. The reaction is continuously proceeding. After the second protonation, one molecule of water comes out and there is formation of carbocation again, which is substituted electrophically in the phenol ring. Let us see how the reaction proceeds:
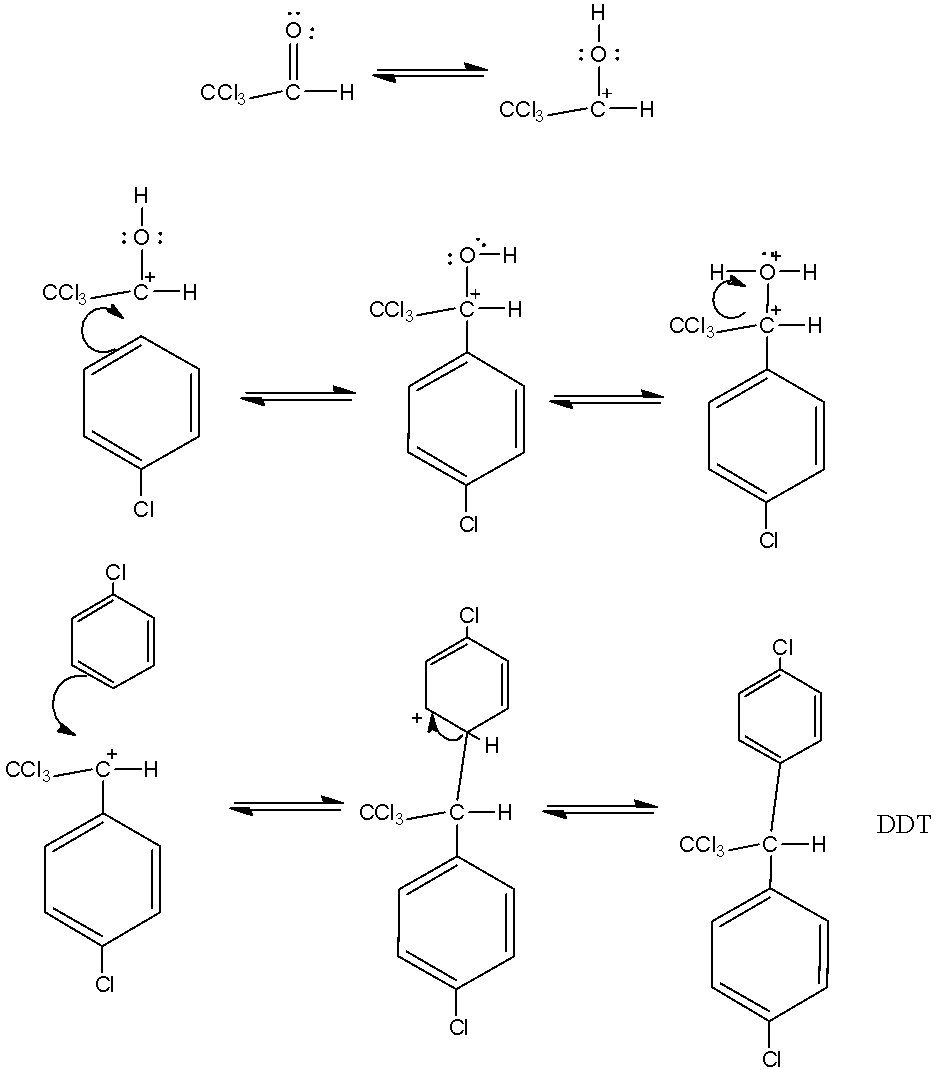
So this is how the reaction proceeds, a series of electrophilic substitution takes place and this is how we obtain the final major product, DDT which is also considered a powerful insecticide.
Note: DDT is a colourless, tasteless and odorless crystalline organic compound. Although it was a good insecticide, it was discontinued for the harmful effects it had on the environment. In the reaction, electrophilic attack occurs on the para position and not the meta position because in the meta position, there is a lot of steric hindrance which causes unstability of the compound. If only one mole of phenol is taken, then steps will reduce and we will not get DDT as the major product.
