Question
Question: Chlorobenzene on fusing with solid \(NaOH\) (at \(623K\) and \(320atm\) pressure) gives: A. benzen...
Chlorobenzene on fusing with solid NaOH (at 623K and 320atm pressure) gives:
A. benzene
B. Benzoic acid
C. phenol
D. benzene chloride
Solution
When it comes to nucleophilic substitution reactions, chlorobenzene is extremely unreactive. This causes the electrons in the C−Cl bond to delocalize, and a partial double bond character develops in the bond, making it difficult for the nucleophile to cleave it.
Complete answer:
When chlorobenzene is fused with solid NaOH , it gives phenol as a product. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of chlorobenzene. Here hydroxide ion replaces chlorine ion from chlorobenzene and gives phenol as a product.
The reaction is as follows:
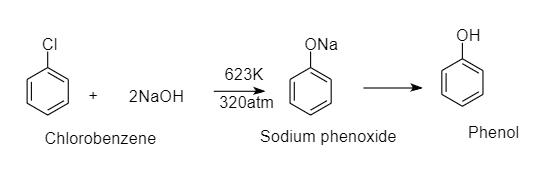
This reaction requires high pressure and temperature since chlorobenzene does not undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions easily.
A nucleophilic substitution reaction is one in which one nucleophile substitutes another in an organic process. It's very similar to normal displacement reactions in chemistry, in which a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element in a salt solution.
Hence, the correct option is C. phenol
Additional Information: The nucleophilicity of a nucleophile is its reactivity or strength in nucleophilic substitution processes. A stronger nucleophile replaces a weaker nucleophile from its component in a nucleophilic substitution process.
Note:
Sodium hydroxide is a white crystalline odourless substance that absorbs moisture from the air at ambient temperature. It's a synthetic chemical. When dissolved in water or neutralised with acid, it releases a significant amount of heat, which could ignite combustible objects. Sodium hydroxide is a highly corrosive substance. It's usually applied as a solid or a 50% solution.
