Question
Question: Chlorination of alkanes is a photochemical process. It is initiated by the process of A. Heteroly...
Chlorination of alkanes is a photochemical process. It is initiated by the process of
A. Heterolysis
B. Homolysis
C. Pyrolysis
D. hydrolysis
Solution
Chlorination of alkanes is a radical substitution reaction. Alkanes react with halogens in presence of sunlight or UV light. The reaction proceeds via a radical chain mechanism.
Complete answer:
Alkanes are extremely stable and inert due to non-polar C-H bond and C-C bond. Due to this unreactive nature of alkanes radical substitution method used for halogenations of alkane.
Chlorination of alkane is a substitution reaction where one hydrogen atom of an alkane is substituted by a chlorine group. As we have given, chlorination of alkanes is a photochemical process. Thus, the reaction is carried out in presence of sunlight or UV light. The three main steps of the mechanism are initiation, propagation and termination.
The first step of the radical chain mechanism is as follows:
Initiation: In presence of UV light Cl-Cl bond undergoes homolytic cleavage and generates two chlorine radicals and initiates the chain process.
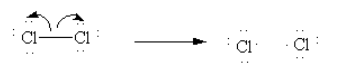
Here, we can see that two electrons in Cl-Cl bonds are equally distributed between the two chlorine atoms after the cleavage of the bond.
If after the cleavage of the bond, the two electrons in bonds are equally distributed between the two bonding atoms it is known as homolysis.
Hence, photochemical chlorination of alkane is initiated by the process of homolysis.
Thus, the correct option is (B) homolysis.
If after the cleavage of the bond, the two electrons in bonds are unequally distributed between the two bonding atoms it is known as heterolysis.
Option (A) is incorrect as two electrons in Cl-Cl bonds are equally distributed between the two chlorine atoms after the cleavage of the bond.
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic compounds. As this is not a pyrolysis reaction so option (C) is incorrect.
Hydrolysis is the addition of a water molecule to an organic compound. As this is not a hydrolysis reaction so option (D) is incorrect.
Note:
Due to less reactivity of alkane, the halogenations reaction takes place only under photochemical conditions. As radicals are unstable so the chlorine radical form in the first step of reaction abstract proton from alkane and give alkyl radical. The alkyl radical again being unstable abstract chlorine atom from chlorine molecule and give chlorine radical. Thus halogenations reaction proceeds.
