Question
Question: Calculate the value of current \[I\] in the given circuit. 
A. 2A
B. 1A
C. 1.5A
D. 5A
Solution
Use the formula for the equivalent resistors connected in series arrangement. Also use the expression for the Ohm’s law. Observe the given circuit diagram and check through which resistors electric current flows. Eliminate the resistors through which the electric current does not flow and draw the equivalent circuit diagram including the resistors through which the current flows. Calculate the equivalent resistance in the circuit and then use Ohm’s law and calculate the value of current.
Formulae used:
The equivalent resistance Req of the two resistors connected in series is given by
Req=R1+R2 …… (1)
Here, R1 and R2 are the resistances of the two resistors.
The expression for Ohm’s law is given by
V=IR …… (2)
Here, V is the potential difference between the two ends of the conductor, I is the current in conductor and R is the resistance of the conductor.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given a circuit diagram consisting of all resistors of resistance 5Ω.From the given circuit diagram, we can see that the potential difference in the given circuit is 15V.
V=15V
Let us redraw the given circuit diagram with names of all the resistors which makes the solution clear about which resistor we are explaining.
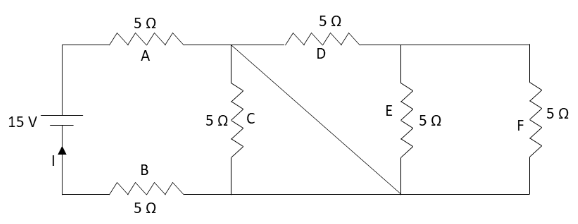
In the above circuit diagram, we can see that the inclined wire in the circuit which has no resistor connected in it is shorting the whole circuit on the right hand side of the inclined wire. Hence, there will not be any current flowing in the resistors named E, E and F. The resistor named C will also receive no current from the circuit as the potential is the same on both sides of the resistor C. So, we can eliminate the resistors C, D, E and F from the given circuit diagram.
The equivalent circuit diagram of the given circuit in which the current flows is as follows:
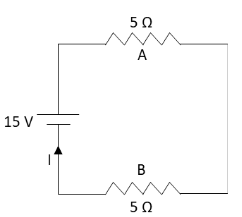
The equivalent resistance in the given circuit is given by equation (1).Substitute 5Ω for R1 and 5Ω for R2 in equation (1).
Req=(5Ω)+(5Ω)
⇒Req=10Ω
Hence, the equivalent resistance in the circuit is 10Ω.
Let us now calculate the current flowing in the circuit using Ohm’s law.Rearrange equation (2) for the current .
I=RV
Substitute 15V for V and 10Ω for R in the above equation.
I=10Ω15V
∴I=1.5A
Therefore, the current in the circuit is 1.5A.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The students should be careful while drawing the equivalent circuit diagram for the given circuit diagram. The students should keep in mind that we should eliminate the whole circuit which is shorted and also the resistors across which the potential difference is zero or the resistors on either sides of which the potential is the same.
