Question
Question: Calculate the potential \(E\) for \(F{{e}^{3+}}|F{{e}^{2+}}\) electrode when the concentration of \(...
Calculate the potential E for Fe3+∣Fe2+ electrode when the concentration of Fe2+ is exactly five times that of Fe3+.
Solution
To find the potential for the given electrode i.e., Fe3+∣Fe2+, first determine the standard electrode potential from the datasheet and with the help of Nernst equation, we can calculate the potential for the given electrode.
Formula used-
E=Eo−n0.059log[R][P]
Where, Eo is the standard electrode potential of the electrode, n is the change in number of electrons during the reaction, [P] is the concentration of ion in product and [R] is the concentration of ion in reactant.
Complete answer:
The value of standard EMF of a cell or potential of the cell when the concentration of species is considered as unity is known as standard electrode potential and it is denoted by Eo. Some basic elements along with their standard electrode potential are given as per following table-
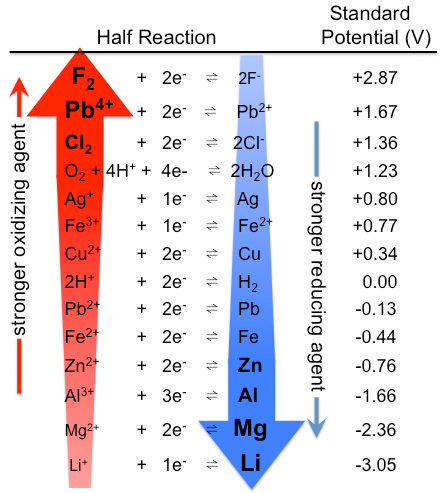
Now, the Fe3+∣Fe2+ electrode can be represented by the following equation:
Fe3++e−→Fe2+
And as per given table, the value for standard electrode potential for the given electrode EFe3+∣Fe2+o=0.77V. We know that the Nernst equation is used to relate reduction potentials to standard electrode potential, temperature and concentration of the species undergoing reduction and oxidation. So, according to the Nernst equation:
E=EFe3+∣Fe2+o−n0.059log[Fe3+][Fe2+]
It is given in the question that the concentration of Fe2+ is exactly five times that of Fe3+ which means [Fe2+]=5×[Fe3+]. Substituting values in the equation:
⇒E=0.77−10.059log[Fe3+]5×[Fe3+]
⇒E=0.77−0.059log5
⇒E=0.73V
Hence, the potential for Fe3+∣Fe2+ electrode under given conditions is 0.73V.
Note:
It is important to note that in this question, the formula used for the Nernst equation is only applicable when the temperature of the reaction is taken as 25oC. As no temperature was mentioned in the question, so here we calculated the potential at room temperature i.e., 25oC. In the case if temperature (other than room temperature) is given then the Nernst equation to be used is E=Eo−nFRTlog[R][P].
