Question
Question: Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in the following gaseous state ions: \( M{n^{3 + }} \) , ...
Calculate the number of unpaired electrons in the following gaseous state ions: Mn3+ , Cr3+ , V3+ and Fe2+ . Which one of these is the most stable in aqueous solutions? (Atomic number of V=23 , Cr=24 , Mn=25 and Fe=26 ).
Solution
Hint : The number of electrons lost or gained by an atom while forming a chemical bond is known as its oxidation state. When the electrons of an atom are present in the lowest possible energy, then it is known as the ground state of an atom whereas when the element is represented with its oxidation state, then it is known as gaseous state or excited state of an ion.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
To calculate the number of unpaired electrons in each gaseous state ion, we need to write the electronic configuration of each element at gaseous state as well as at excited state.
Manganese (Mn):
Atomic number =25
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom =[Ar]3d54s2
At the +3 oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of Mn3+ ion will be as follows:
Mn3+=[Ar]3d44s0
Orbital representation for electrons of Mn3+ ion will be as follows:
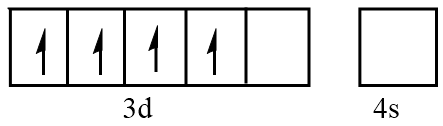
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in Mn3+=4
Chromium (Cr):
Atomic number =24
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom =[Ar]3d54s1
At the +3 oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of Cr3+ ion will be as follows:
Cr3+=[Ar]3d34s0
Orbital representation for electrons of Cr3+ ion will be as follows:
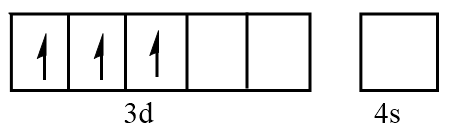
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in Cr3+=3
Vanadium (V):
Atomic number =23
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom =[Ar]3d34s2
At the +3 oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of V3+ ion will be as follows:
V3+=[Ar]3d24s0
Orbital representation for electrons of V3+ ion will be as follows:
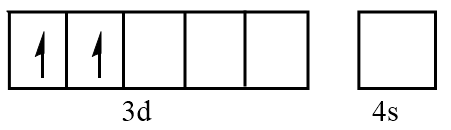
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in V3+=2
Iron (Fe):
Atomic number =26
Electronic configuration at ground state of the atom =[Ar]3d64s2
At the +2 oxidation state, removal of three electrons will take place from the valence shell of the atom. Hence the electronic configuration of Fe2+ ion will be as follows:
Fe2+=[Ar]3d64s0
Orbital representation for electrons of Fe2+ ion will be as follows:
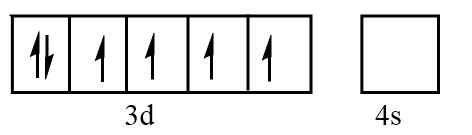
Hence, the number of unpaired electrons in Fe2+=4
Now, among the given gaseous state ions the most stable ion in aqueous solution will be Cr3+ ion because it has three unpaired electrons and on splitting of d-orbital, the t2g orbital will be half-filled which leads to increase the stability of the ion.
Note :
It is important to note that when electrons of ligands reach the d-orbital of metals, the d-orbitals closer to the ligands will have comparatively higher energy than those which are further away. So, due to electronic repulsions the splitting of d-orbital takes place. Also, half-filled and completely filled orbitals are more stable than partially filled d-orbitals.
