Question
Question: Calculate the number of fringes in 
Solution
The given question is an application of Young’s double-slit experiment. The fringes are seen due to the interference pattern caused as a result of overlapping light waves from the two slits.
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the given fig,
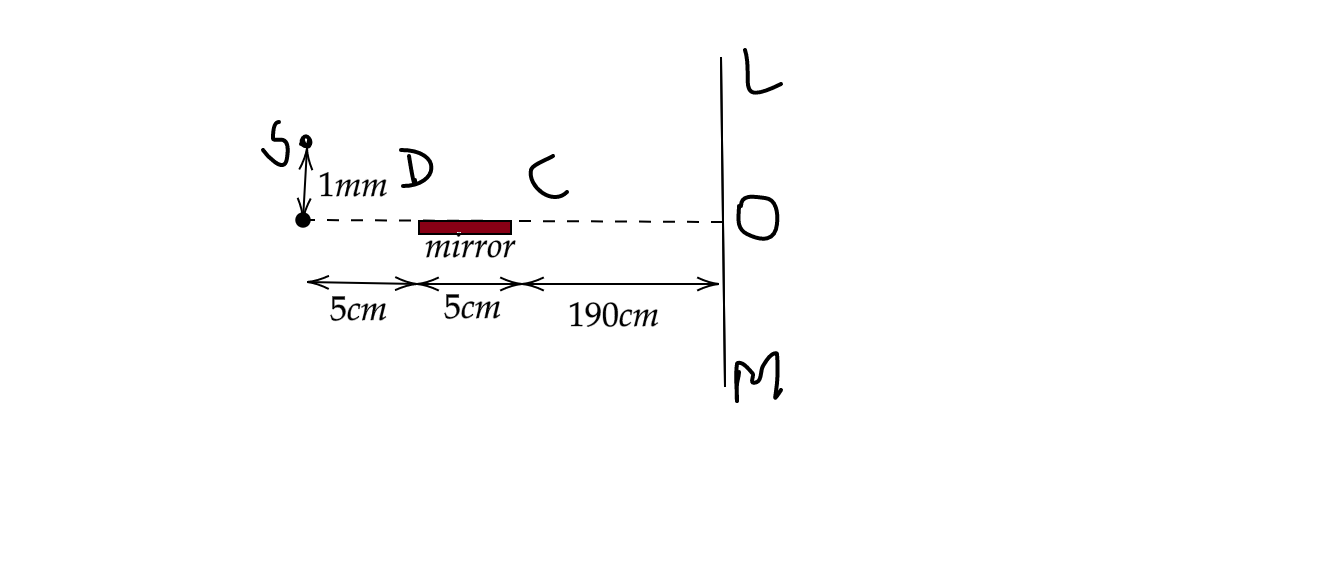
S is a point source of light
DC is the mirror
The rays from S get reflected on the mirror at points D and C and reach the screen at L and N
Thus, LN is the region in which fringes are visible.
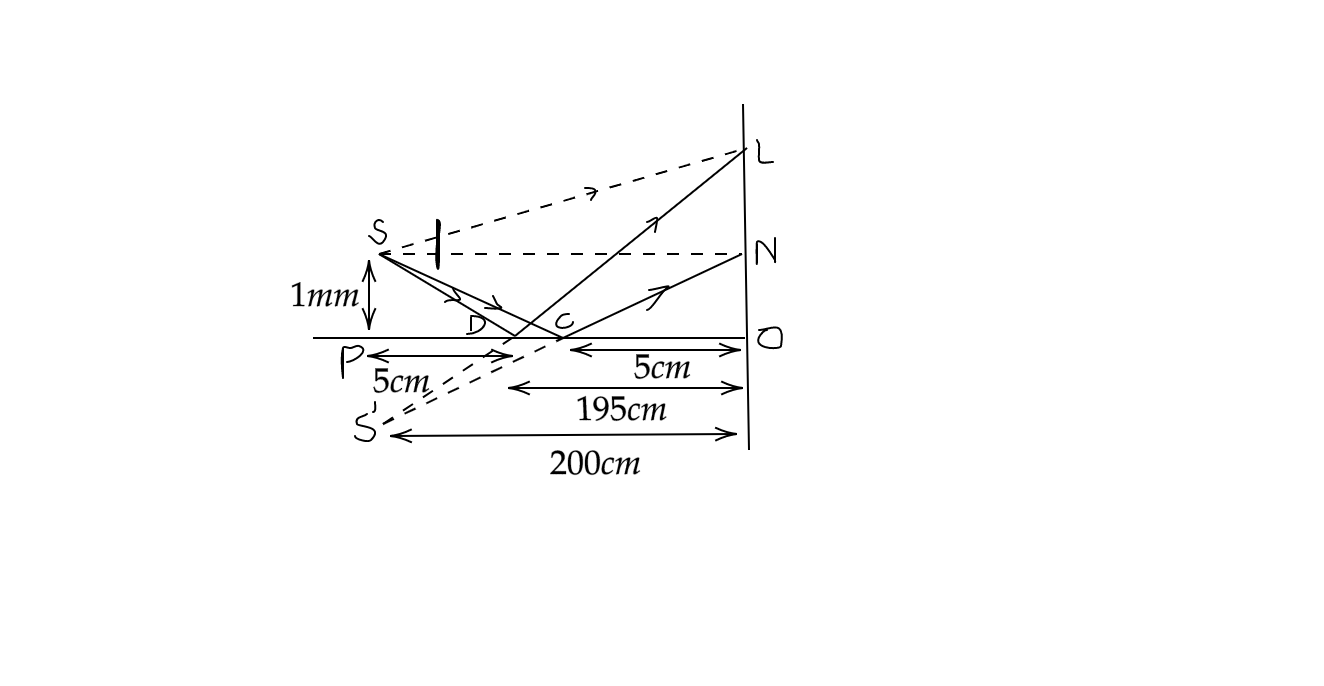
From the triangles SDP and LDO, using properties of similar triangles, we can state that
y2=39mm
Now, from the triangles SCP and NCO, using properties of similar triangles, we can say that
y1=19mm
Thus, the width of fringe visibility is LN, as stated above,
LN =y2−y1=20mm=2cm
The width of the fringe β=0.05cm
Hence, we can also conclude that in interference, fringe width is constant for all fringes.
Now, the number of fringes can be seen by us is given as the ratio of the width of fringe visibility (which is nothing but the effective screen width) to the width of a single fringe, that is,
