Question
Question: Calculate the lattice energy of a salt \[MX(s)\] from the date given below: Heat of formation of ...
Calculate the lattice energy of a salt MX(s) from the date given below:
Heat of formation of MX(ΔH)=−550kJ/mol
Heat of sublimation of M(S)=80kJ/mol
Heat of dissociation of X2(D)=155kJ/mol
Ionization energy of M(IE)=347kJ/mol
Electron affinity of X(EA)=−343kJ/mol
A. −835KJ/mol
B. −938.5 kJ/mol
C. −711.5 kJ/mol
D. −638.5 kJ/mol
Solution
Born Haber cycle is mainly used to calculate the lattice energy. It also involves steps such as sublimation energy (ΔHsub), dissociation energy (D), ionisation energy(I), electron affinity(E) and heat of formation of crystal (H). Represented in the form of
Δ Hf0= ΔHsub+ 2D+ IE + EA+U
Complete step by step answer:
Born Haber cycle is a cycle of enthalpy change of process and The energy terms involved in building a crystal lattice( MX) such as -
Step1 - convert solid ( M) to gaseous ( M)is called enthalpy of sublimation (ΔHsub).
Step 2 - convert gaseous(X) molecule to atoms is called enthalpy of dissociation(D).
Step 3 - Conversion of gaseous ( M) atom into (M ion) in gaseous state is called ionisation energy .
Step 4 - Conversion of gaseous (X) atom into gaseous X ion is known as electron gain enthalpy and represented by EA.
Step 5 - The amount of energy released when one mole of solid crystalline compound is obtained from gaseous ions is called lattice energy(U)
M(s)+ 21X(g)→MX(s)
The Born-Haber Cycle can be reduced to a single equation:
Heat of formation= Heat of atomization + Dissociation energy+ (sum of Ionization energies) + (sum of Electron affinities)+ Lattice energy
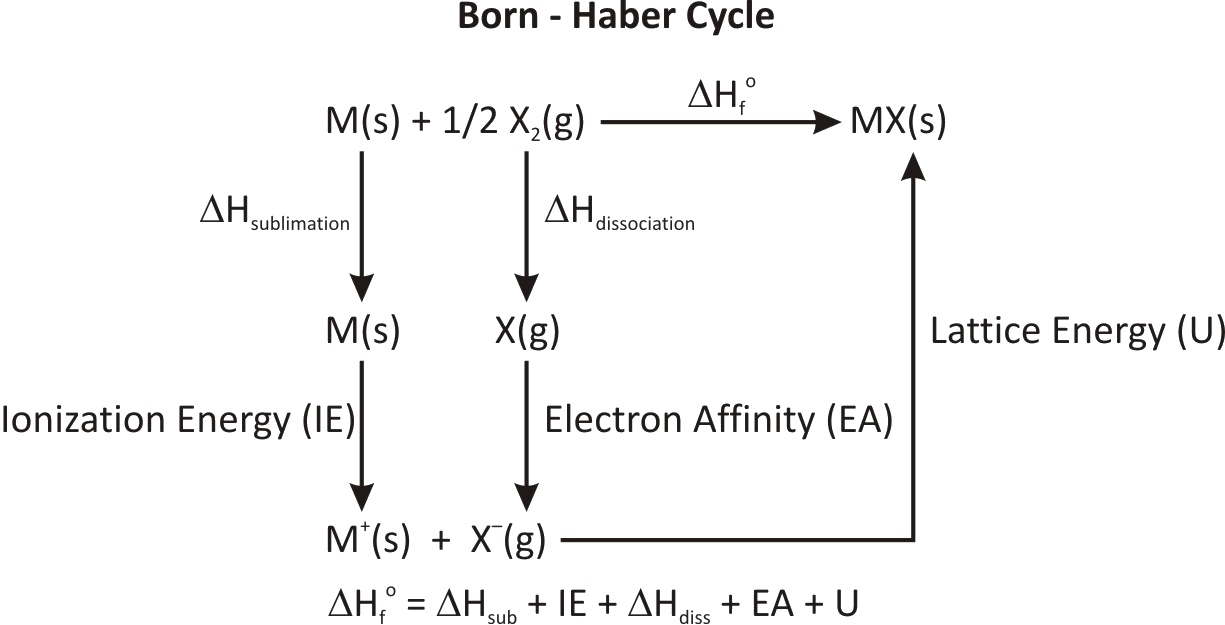
The enthalpies are represented in figure.
These steps are represented as -
Δ Hf0= ΔHsub+ D/2 + IE + EA+U
Now, Putting values as -
ΔHf=S + 0.5D + IE + EA + U
−550 =80+2155+347−343+U
U=−711.5kJ/mol
lattice energy of salt =−711.5kJ/mol.
Option (c ) is correct.
Note: Born Haber process is a method that allows us to observe and analyze energies in a reaction. It mainly helps in describing the formation of ionic compounds from different elements. Born Haber cycle is a process that leads to the formation of a solid crystalline ionic compound from the elemental atoms in their standard state and of the enthalpy of formation of the solid compound such that the net enthalpy becomes zero.
