Question
Question: Calculate the equivalent mass of \[HCl\] in the given reaction: \[{K_2}C{r_2}{O_7} + 14HCl \to 2KCl ...
Calculate the equivalent mass of HCl in the given reaction: K2Cr2O7+14HCl→2KCl+2CrCl3+3Cl2+H2O.
Solution
The given reaction between hydrochloric acid and potassium dichromate is a redox reaction. The equivalent mass of hydrogen chloride can be calculated by knowing its molecular mass and its n−factor in this particular reaction.
Complete answer:
The n−factor is a number that measures the change in electrons taking place per molecule. The electrons in the process can be gained (reduction) as well as lost (oxidation). But in a balanced redox reaction we observe that the number of electrons being gained or lost as a result of oxidation or reduction are the same.
In the reaction between hydrochloric acid and potassium dichromate, the dichromate ion is being reduced to Cr3+ ions and the chloride ions are being oxidized into diatomic chlorine gas molecules with a zero oxidation state. The balanced redox reaction can be written as follows:
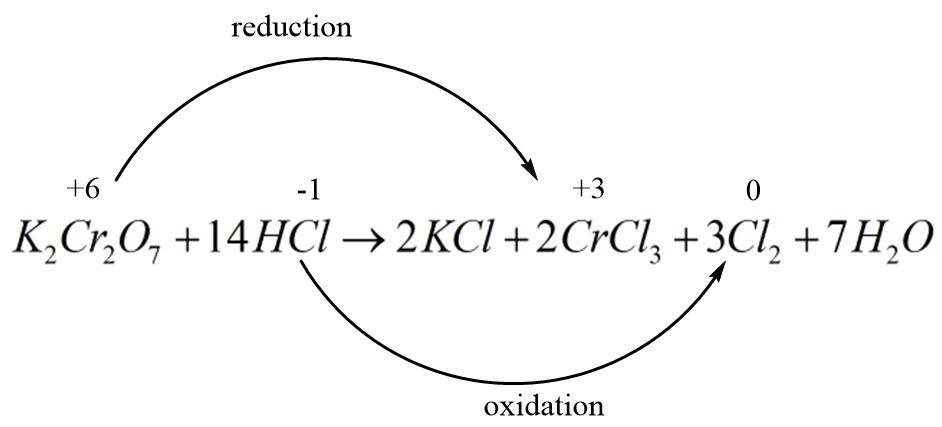
In order to find out the n−factor of HCl, we need to break the reaction into two halves where one represents the oxidation half and the other represents the reduction half. Each half must be written with the number of electrons involved in the process in such a way that the oxidation numbers get balanced.
a.Oxidation
2Cl−→Cl2+2e−
b.Reduction
Cr(VI)→Cr3++3e−
The electrons gained and lost in a balanced redox reaction must be equal. Hence the oxidation reaction is multiplied by three and the reduction reaction is multiplied by two.
6Cl−→3Cl2+6e−
2Cr(VI)→2Cr3++6e−
Thus there are six electrons being involved in the redox reaction for fourteen HCl molecules (the stoichiometric number of HCl in the balanced reaction).
The formula of n−factor calculation is given as follows:
n−factor=number of molecules involvednumber of electrons involved
Putting the number of involved electrons as six and number of involved molecules as fourteen in the above formula we get,
n−factor=146
The equivalent mass can be calculated by finding out the ratio of the molar mass and n−factor of hydrogen chloride
equivalent mass=n−factormolecular mass of HCl
equivalent mass=14636.5
Which when simplified gives,
equivalent mass HCl=85.17amu
Hence, the equivalent mass of HCl in the given reaction is 85.17amu.
Note:
The oxidation numbers assigned to atoms in the chemical equation are hypothetical numbers that represent the number of electrons donated by or accepted by that atom in making bonds with the atoms present in the molecule.
