Question
Question: Calculate the critical angle for glass air interface if a ray of light incident on a glass surface i...
Calculate the critical angle for glass air interface if a ray of light incident on a glass surface is deviated through 15˚ when angle incident is 45˚.

Solution
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of sine of angle incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of given color and for the given pair of media. This constant is also called the refractive index of the second medium with respect to the first.
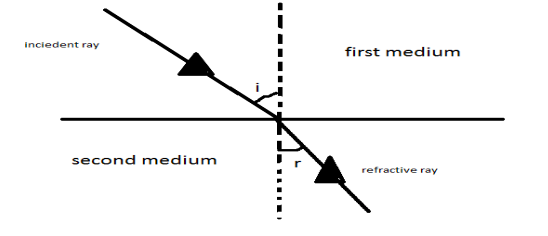
Formula used: When the ray of light enters the second medium through the fist medium.
μ=sin(r)sin(i)
Where, µ is the refractive index of glass.
‘i’ is the angle of incidence and ‘r’ is the angle of refraction.
Step by step solution:-
(a).
Given that,
Incident angle, deviated rays .
Let critical angle be ic.
Now,
sin ic=μ
Where, μ is the refractive index of glass.
Now, again i=r& sin isin r=μ
⇒μ=22
⇒μ=2
⇒μ=1.4
Now, the critical angle is
sinic=μ1
⇒sinic=1.41
⇒sinic=0.71
⇒ic=sin−1(0.71)
Hence, the critical angle is 45∘.
Note :- Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through a boundary between two different isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air. In optics, the law is used in ray tracing to compute the angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to find the refractive index of a material.
