Question
Question: Calculate the bond order of \( O_{2}^{+} \) and \( O_{2}^{-} \)...
Calculate the bond order of O2+ and O2−
Solution
Hint : We know that first draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram. To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is: Bond order = 21[Bonding − antibonding]
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let’s first draw the MOT of the oxygen molecule. The oxygen molecule contains the 16 electrons. The bond order may be defined as half the difference between the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals (Nonbonding) and the number of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital.
And for O2−
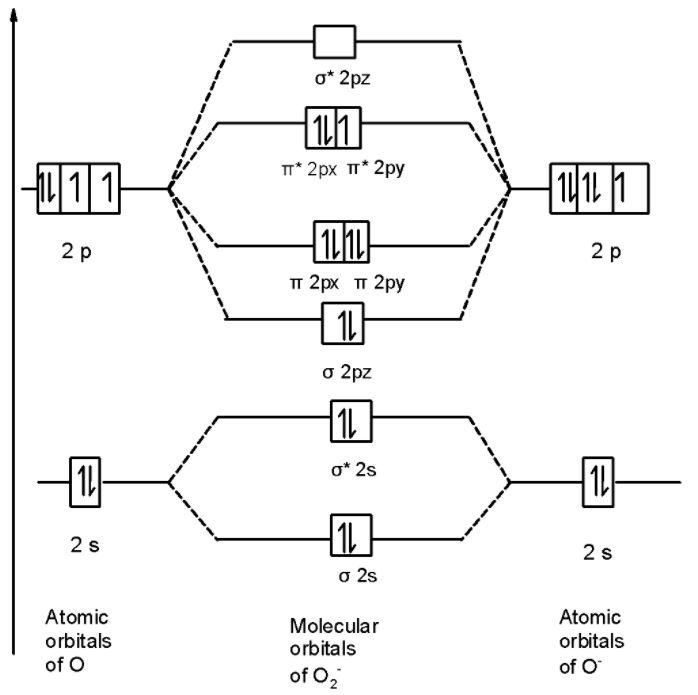
And for O2+
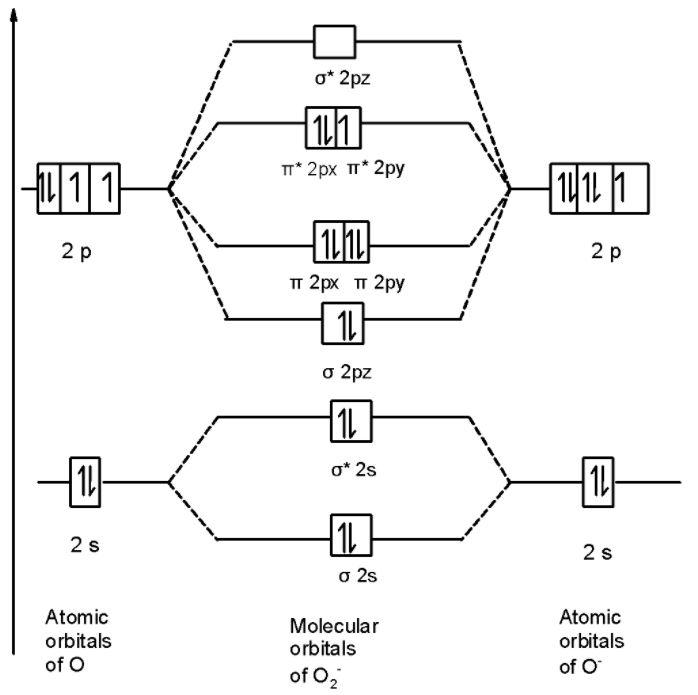
Let us calculate the bond order
Bond order (B.O) 21× [Number of an electron in antibonding molecular orbitals] – [Number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals]
The higher the order of the bond the greater the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the length of the bond.
B.O for O2 =21×[106]=2.
B.O for O2−=21×[10−7]=1.5
B.O for O2+ =21×[10−5]=2.5
B.O for O22− =21×[108]=1
Therefore, the increasing order of bond length for these species is O2+ <O2 <O2− <O22−
Note :
Remember that you should notice that bond order is indirectly proportional to the length of the bond. The higher the bond order, the shorter and stronger will be the bond. The addition of each electron in the antibonding molecular orbital will decrease the bond order.
