Question
Question: Calculate CFSE of the following complex: \({{\left[ Co{{F}_{6}} \right]}^{3-}}\) (A) −0.4 \({{\D...
Calculate CFSE of the following complex:
[CoF6]3−
(A) −0.4 Δo
(B) 0.4 Δo
(C) −0.4 Δt
(D) 0.6 Δt
Solution
The given complex is characterized by a smaller crystal field. As a result, instead of pairing with another electron, electrons choose to occupy the higher d orbitals. From this we can calculate the number of electrons in different orbitals and it will give us the value of CFSE.
Complete step by step solution:
- According to crystal field theory, an octahedral complex which has six ligands systematically arranged around a central atom. Hence, we can assume that the given complex [CoF6]3−is an octahedral complex.
- In an octahedral complex, the d orbitals are split into t2g and eg.Here the t2g orbitals will be lower in energy compared to egorbitals. The splitting can be shown as follows,
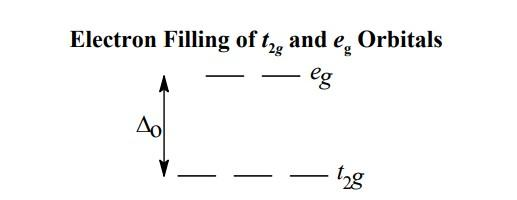
- Let's find the oxidation state of cobalt(x) in [CoF6]3−.We know fluorine has a charge of −1.
x−6=−3
∴ x=+3
Thus, Co exists as Co3+. Its outer electronic configuration can be given as3d64s0. The arrangement of these 3d electrons will determine the crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE). There are two possible fillings in the t2g and eg orbitals for electronic configuration from d4 to d7 .
- There is a high spin configuration which minimizes the pairing of electrons by spreading them across the two orbitals and there is a low spin configuration which minimizes the occupancy of electrons in eg by the pairing of electrons in t2gitself.
- CFSE of an octahedral complex is given by,
CFSE =(−0.4×nt2g)+(0.6neg)Δo
Where nt2g is the number of electrons occupied in t2g orbital and neg is the number of electrons occupied in eg orbital.
- From the spectrochemical series it's clear that F−is a weak field ligand and thus it will give rise to the high spin complex. Therefore, the electrons will spread in both orbitals giving rise to the configuration of t42ge2g. This implies that there are four electrons in t2g orbital and two in egorbital. Thus, CFSE can be found as follows
CFSE = (−0.4×4) +(0.6×2)
= −1.6+1.2
= −0.4 Δo
Therefore, the answer is option (A) −0.4Δo.
Note: As we mentioned above, the spectrochemical series plays an important role in determining whether the complex is high spin or low spin. It can be represented as follows
I−< Br−< Cl−< F−< OH−< C2O42−< H2O< NH3< en< bipy< phen< CN−≈CO. Ligands up to water are generally weak ligands and thus form high spin complexes and ligands beyond water are strong field ligands and they form low spin complexes.
