Question
Question: \(C{O_2}\) has the same geometry as: i.\(HgC{l_2}\). ii.\(N{O_2}\) iii.\(SnC{l_2}\) iv.\[{C...
CO2 has the same geometry as:
i.HgCl2.
ii.NO2
iii.SnCl2
iv.C2H2
A.i and ii
B.ii and iv
C.i and iv
D.iii and iv
Solution
CO2 has linear geometry as it has two electron groups and no lone pairs. So, we will draw the geometry of CO2 and come to know that as it has no lone pair, shape and geometry will be the same that is linear and now we have to see whether other molecules have lone pairs present or not.
Complete step by step answer:
There are two main factors that determine the geometry of a molecule:
The number of bonding electron pairs around the central atom.
These outer shell or valence shell electrons will try to sit themselves as far as possible from one another as to reduce the electron repulsion or as to attain maximum stability.
As to find the molecular geometry firstly we need to draw Lewis dot structure of the molecule.
CO2 has linear geometry , because there are no lone pairs that will affect the orientation of the molecule.
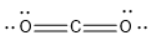
HgCl2 has linear geometry , because there are no lone pairs that will affect the orientation of the molecule.
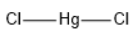
NO2 has bent geometry, because there are lone pairs that will affect the orientation of the molecule.
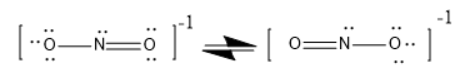
It is in resonance.
SnCl2 has linear geometry , because there are lone pair that will affect the orientation of the molecule.
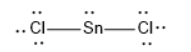
C2H2 has linear geometry , because there are no lone pairs that will affect the orientation of the molecule.
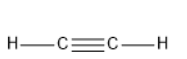
Therefore, option C is correct.
CO2 has the same geometry as HgCl2and C2H2.
Note:
Geometry of a molecule can be explained by the arrangement of lone pair and bond pairs while shape can be explained by the arrangement of atoms around the atoms, it is not linked with lone pair and hence only deals with bond pairs.
