Question
Question: \(C{{O}_{2}}\) and \(Si{{O}_{2}}\) is a solid or gas? (A) \(C{{O}_{2}}\) gas and \(Si{{O}_{2}}\...
CO2 and SiO2 is a solid or gas?
(A) CO2 gas and SiO2 solid
(B) CO2 solid and SiO2 gas
(C) CO2 gas and SiO2 gas
Solution
Both carbon and silicon belong to the same group in the periodic table and this means that these atoms have similar properties. CO2 consists of a carbon atom which is covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms and SiO2 or silicon dioxide is an oxide of silicon.
Complete answer:
-As we know, both carbon and silicon belong to the same group in the periodic table. Hence, both these atoms should have similar properties. These atoms have a tendency to show catenation which is the property of an element with which it can form a long chain by linking with other atoms of the same element.
- In carbon dioxide there is a double bond between the oxygen and carbon atoms. (O=C=O), each molecule is attracted to the other molecules through the London forces or van der waals forces.
- Because of the small atomic size, carbon atom possesses partial triple bond character with the neighboring oxygen atoms and due to the linear structure CO2 is non-polar and hence they exhibit weak van der waals forces. As a result, Carbon dioxide (CO2 ) exists as gas.
- In the case of SiO2, every silicon atom is covalently bonded to four oxygen atoms and every oxygen atom is bonded to two silicon atoms. This will result in the formation of a giant tetrahedral structure which is shown below
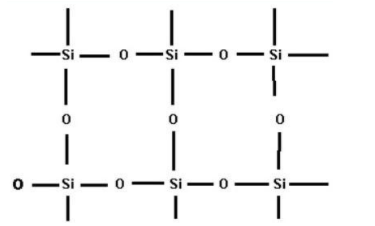
Because of this giant network, the bonding in SiO2 is very strong and thus it exists as a solid. Therefore the CO2 molecule exists as gas and SiO2 exists as solid.
Thus the answer is option (A) CO2 gas and SiO2 solid.
Note: It should be noted that, CO2 is an acidic oxide (forms carbonic acid on reaction with water) and SiO2 doesn’t react with water, due to the difficulty of breaking up the giant covalent structure. Instead, SiO2 is very weakly acidic when reacting with bases.
