Question
Question: \(C{{H}_{3}}CHO\xrightarrow[\left( 2 \right){{H}_{2}}O]{\left( 1 \right)C{{H}_{3}}MgBr}\left( A \rig...
CH3CHO(1)CH3MgBr(2)H2O(A)H2SO4,Δ(B)hydroborationoxidation(C)
Compound A and C in the given reaction are:
A) Identical
B) Positional isomers
C) Functional isomers
D) Optical isomers
Solution
When a substance has the same number of atoms in every element but has a different arrangement, then it is known as isomers. It is not necessary that the isomers will show the same physical and chemical properties. There are many isomers like positional isomer, functional isomer, identical isomer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When an acetaldehyde reacts with methyl magnesium bromide it results in the formation of propan −2− ol. This is product A. The organometallic reagent having nucleophilic carbon adds to the carbonyl group of the electrophilic carbon, carbonyl group having electrons move to the electronegative oxygen and form an intermediate of metal alkoxide complex.
After that protonation takes place, which converts the alkoxide complex into an alcohol. Propan −2− ol heated in presence of sulphuric acid and undergoes dehydration to form 1− propene. This product B. When hydroboration oxidation takes place for 1− propene , the hydroxyl group will attach on less substituted carbon and result in the formation of propan −1− ol. This product is C.
In this question, the compound A and C formed are positional isomers because they contain the same carbon skeleton and same functional group but they differ in the location of the functional group. In compound A the alcohol is attached to second carbon whereas in compound C , the alcohol is attached to first carbon.
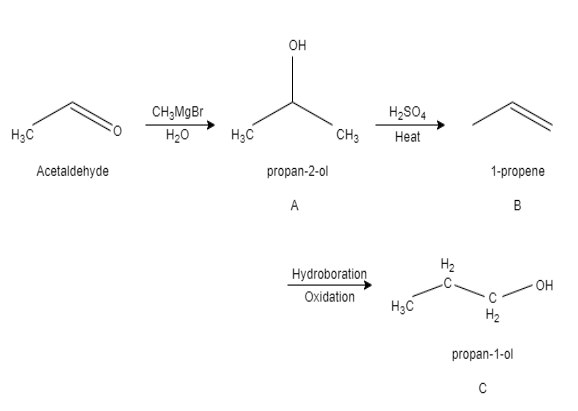
Therefore option B is the correct answer.
Note: In hydroboration oxidation, alkene is converted into an alcohol. It is a two step hydration reaction which follows anti markovnikov rule, the hydroxyl group is attached to less substituted carbon . In the first step, borane is added to the double bond and results in the formation of trialkylborane. In the second step, trialkylborane is treated with hydrogen peroxide.
