Question
Question: C{H_3}C{H_2}COOH\xrightarrow[{{\text{Red P}}}]{{B{r_2}}}X\xrightarrow{{N{H_3}}}Y \( \) Y $ in th...
C{H_3}C{H_2}COOH\xrightarrow[{{\text{Red P}}}]{{B{r_2}}}X\xrightarrow{{N{H_3}}}Y Y $ in the above reaction is:
(A) Lactic acid
(B) Ethylamine
(C) Propyl amine
(D) Alanine
Solution
We have given the reaction sequence in which the product of the first reaction acts as a substrate for the second reaction. The first part of the given reaction sequence is known as the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction or HVZ reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Now first we will understand the first step of the reaction sequence which is known as the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction. According to Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction when carboxylic acid is treated with halogens like chlorine or bromine in the presence of red phosphorous then the α−H or alpha hydrogen atom of a carboxylic acid is replaced by the halogen atom chlorine or bromine to form α− Halo acid. This overall reaction is known as the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction.
Now we will complete the given reaction sequence. So, the reaction will be as follows.
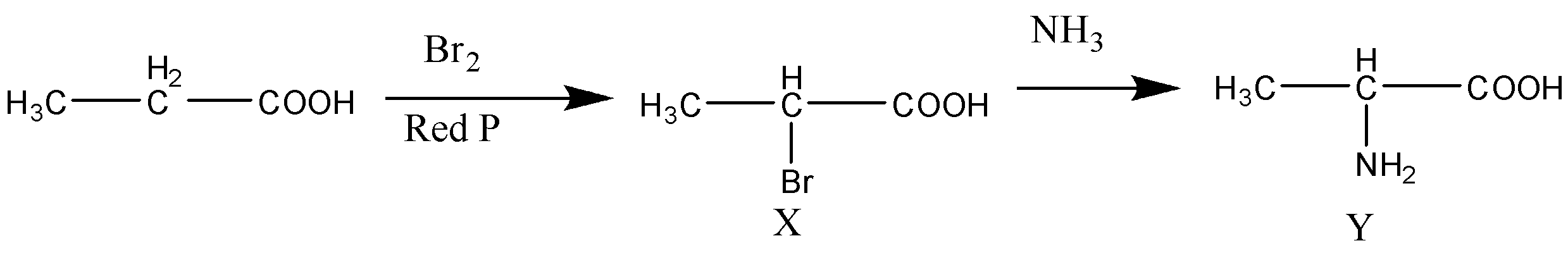
Now we can observe the reaction properly, the first reaction is the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction or HVZ reaction in which α− Halo acid is formed. In the Hell Volhard Zelinsky reaction, the product is formed α− bromopropionic acid. Now when α− bromopropionic acid is reacted with ammonia or alcoholic ammonia the reaction proceeds with the removal of hydrogen bromide and the final product formed is 2− amino propionic acid which is commonly known as alanine. So, now we can conclude that the products X and Y are X→CH3CH(Br)COOH and Y→CH3CH(NH2)COOH .
Therefore, the correct option is (D).
Note:
It may be noted that bromination exclusively occurs at the α− position and the reaction stops after all the α− hydrogens have been replaced by the bromine atoms. In contrast, chlorination can proceed after α− halogenation to other positions.
