Question
Question: \(C{H_3}C{H_2}Br\xrightarrow{{aqKOH}}A\xrightarrow{{KMn{O_4}/{H^ + }}}B\xrightarrow[\vartriangle ]{{...
CH3CH2BraqKOHAKMnO4/H+BNH3△CBr2alkaliD . D is:
A) CH3Br
B) CH3CONH2
C) CH2NH2
D) CH2Br2
Solution
Reagents used in the conversion are very important. The aqKOH use, carry out nucleophilic substitution reaction while KMnO4/H+ is a very strong oxidizing agent. The ammonia (NH3) easily takes up protons in the reaction and BH2 /alkali is a reagent used in Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
CH3CH2BraqKOHAKMnO4/H+BNH3△CBr2alkaliD
First of all, let us break the sequential conversion, in order to make the conversion process easier for us.
Let us first look at this part of the reaction CH3CH2BraqKOHA.
aqKOH acts a nucleophile here and the reaction is a bimolecular nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2 reaction) as the ethyl bromide is a primary alkyl halide. Thus, we get
CH3CH2−BraqKOHCH3−CH−OH
The ethanol formed in the reaction is then oxidized by acidified potassium permanganate to give the corresponding carboxylic acid.
That is,
CH3−CH2−OHKMnO4/H+CH3−COOH
The NH3 then takes up proton from the carboxylic forming ammonium ethanoate which when heated gives ethanamide.
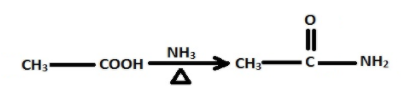
The ethanamide then reacts with BH2 /alkali to form methylamine.
CH3−CONH2BH2alkaliCH3NH2
This is Hoffmann bromamide reaction. The amide formed contains one carbon atom less than amide.
Thus, the sequential conversion can be written as –
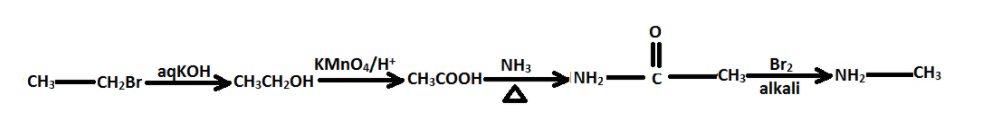
Option (C) is the correct option.
Note:
Students should understand that associated colloids, also called micelles, are generally electrolytes. They exist as ions at low concentration. It is above a particular concentration called critical micelle concentration (CMC) and above a temperature called Kraft temperature; these get associated and exhibit colloidal behavior. It is very important to note that the primary distinguishing features between a true solution and a colloidal solution is fundamentally the dimension of the constituent part.
