Question
Question: \({{C}_{6}}{{H}_{5}}C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{Cr{{O}_{2}}C{{l}_{2}}}Z\) In the given sequence, \(Z\) ...
C6H5CH3CrO2Cl2Z
In the given sequence, Z is:
A) Benzaldehyde
B) Toluic acid
C) Phenol acetic acid
D) Benzoic acid
Solution
The chemical formula C6H5CH3 indicates toluene (methyl group attached to benzene ring. The chemical CrO2Cl2 is a mild oxidising agent. Hence, the above reaction shows the mild oxidation of Toluene, which means either hydrogen will be removed or oxygen will be added or both.
Complete answer:
Here, we are given a compound by the chemical formula C6H5CH3 . Now we know that the C6H5− component shows a benzene ring. Hence, the given compound is Toluene whose structural formula is given as,
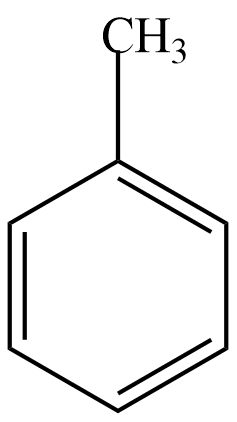
Now, the catalyst given here is CrO2Cl2 which acts as a mild oxidising agent. Hence, we can understand the reaction will give the oxidised product of toluene.
Now, if toluene is viewed through a methyl group, it can be seen as a primary alkane. We know that oxidation of a primary alkane gives alcohol which on further oxidation gives aldehyde, which on further oxidation gives carboxylic acid.
However, if the oxidising agent is weak or in limited quantity, the oxidation stops at aldehyde. As here we are using a mild oxidising agent, hence we will get an aldehyde as a final product.
Now, the oxidation of toluene in presence of oxidising agent to produce aldehyde is shown as
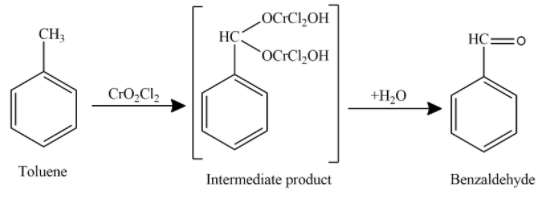
Hence, the final product obtained is Benzaldehyde. This reaction is known as Etard’s reaction
Hence, the final answer is Option (A)
Note: This reaction is used for the laboratory preparation of Benzaldehyde. Here, the oxidizing agent CrO2Cl2 is a mild oxidising agent. We can also use CrO3 combined with (CH3CO)2O as a mild oxidising agent. Whenever we are required to prepare aldehyde from alkane, we need a mild oxidising agent. A strong oxidising agent will carry the oxidation further and produce carboxylic acid from aldehyde.
