Question
Question: By what factor will the rate constant for the reverse catalysed reaction increase compared to that f...
By what factor will the rate constant for the reverse catalysed reaction increase compared to that for the reverse uncatalysed reaction.
Solution
The Arrhenius equation is an equation that represents the relationship between the temperature of many physical and chemical reactions with the rate of the reaction. In other words, the Arrhenius equation gives the dependence of the rate constant of a chemical reaction on the absolute temperature. Arrhenius equation helps in determining the rate of chemical reactions and their activation energies too.
Complete answer:
Step 1: Identifying the values of various components of the Arrhenius equation for a reverse catalyzed reaction:
For the reaction:
2H2O2→2H2O+O2
Arrhenius equation is equal to
k=AeRT−Ea
Where, Ea is the activation energy while R is the universal gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature.
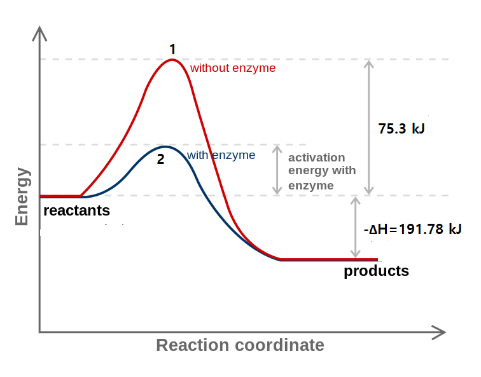
Form the figure, for backward reaction the value of activation energy is
Ea1=75.3+∣ΔH∣=75.3+191.78 kJ/mol = 267.08×103 J/mol
Ea2 = 56.6+∣ΔH∣=56.6+191.78 kJ/mol= 248.38×103 J/mol
T= 298K and R=8.314 J K−1mol−1
Step 2: Solving the Arrhenius equation by substituting the values:
k2k1=AeRT−Ea2AeRT−Ea1
⇒k2k1=eRTEa1−Ea2
⇒k2k1=e8.314×298(267.08−248.28)×103
⇒k2k1=e7.54
⇒k2k1=1896.4
Therefore, by the factor of 1896.4, the rate constant increases in a reverse catalyzed reaction.
Note:
Catalyst is a substance that alters the rate of reaction without itself undergoing any change or without itself participating in the reaction. Moreover, a catalyst lowers the activation energy required for a reaction to proceed thereby speeding up the reaction. Also, a catalyst can accelerate a reaction by reducing the rate-limiting transition state. The addition of a catalyst alters the reaction pathway and as the reaction pathway is changed, the activation energy for both forward and reverse reaction decreases but the frequency factor increases.
