Question
Question: \( Butan - 2 - ol \) is an example of:...
Butan−2−ol is an example of:
Solution
Hint : There are various functional groups such as carboxylic acids, alcohols, phenols, carbonyls, etc. Alcohols are organic compounds and referred to as a functional group which contains at least one hydroxyl group (−OH) is present at saturated carbon atoms. Alcohols can be mainly of three types such as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
We know that there are various functional groups which have different physical and chemical properties. Alcohol is one of them. Therefore, alcohols are the organic compounds which contain at least one hydroxyl group (−OH) at a saturated carbon atom. Their IUPAC naming is done by placing a suffix “-ol” to the name of the compound.
Now, if we consider the given compound Butan−2−ol , it has “-ol” as a suffix, so, we can say that the compound given is an alcohol.
We know that, there are three types of alcohols such as primary alcohols (which have one alkyl substituent), secondary alcohols (which have two alkyl substituents on the alcoholic carbon) and the tertiary alcohols (which have three alkyl substituents on the alcoholic carbon atom).
Now, we will see the structure of Butan−2−ol :
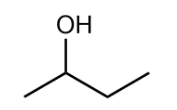
In this the alcoholic carbon is attached to two alkyl substituents and hence, it is a secondary alcohol group.
Hence, from the above observations, we can say that Butan−2−ol is an example of secondary alcohol.
Note :
Butan−2−ol has many applications such as, it is used as a solvent and chromatography reagent. It is used for the preparation of intermediates of methyl ethyl ketone, butyl acetate, sec-butyl and also can be used as plasticizers, herbicides, solvents and processing agents and many more.
