Question
Question: Bromination of 2- butene dioic acid gives: A. (2R,3S)- 2, 3 dibromo succinic acid B. (2R,3R)- 23...
Bromination of 2- butene dioic acid gives:
A. (2R,3S)- 2, 3 dibromo succinic acid
B. (2R,3R)- 23 dibromo succinic acid
C. A mixture of (2R,3R) and (2S,3S) – 2, 3 dibromo succinic acid
D. (2S,3S)-2,3 dibromo succinic acid
Solution
Treatment of alkenes with bromine gives vicinal dibromides. Attack of the alkene in bromine gives the bromonium ion, which is attacked at the backside by bromide ion to give the trans dibromo product. Note that the bromines are delivered to opposite sides of the alkenes. The two atoms that form a new bond to carbon add to the opposite faces of the alkene. This is a stereo selective reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
Alkenes react with bromine in the cold with organic solvent. The bond breaks, a bromine atom becomes attached with each carbon. The bromine loses its original red brown color to give a colorless liquid. Bromination is the example of electrophilic addition. The bromine is a very polarized molecule and the approaching pi bond in the alkene induces a dipole in the bromine molecule.
Here the configuration of Bromination of 2- butene dioic acid is (2R,3S)- 2, 3 dibromo succinic acid or (2S, 3R)-2,3- dibromo succinic acid.
The reaction is given below:
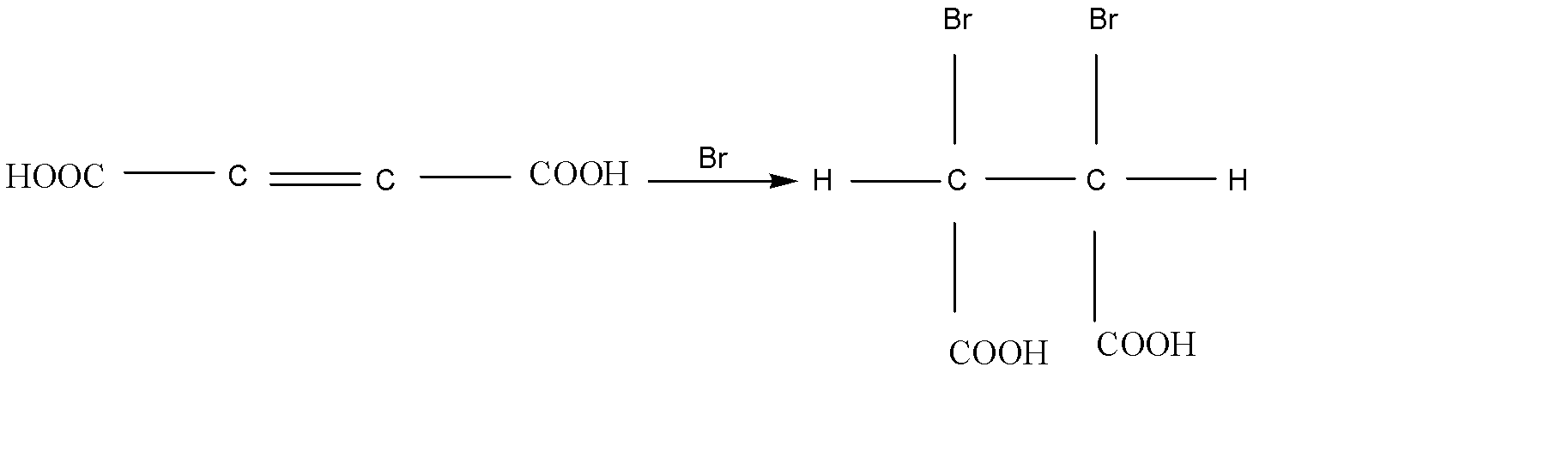
Therefore, option (A) is the correct answer.
Note: Consider using the reaction for this species. All reactions involving this species. A general reaction form is also available. If Bromination occurs on an alkene adjacent to an aromatic ring, some products that appear to have been produced from syn Bromination observed. This is particularly true in any case where a long lived, stable carbocation can be formed.
