Question
Question: Bring about the following conversion: Trans-1,2-diphenyl ethylene \[\to \] Cis-1,2-diphenyl acetyl...
Bring about the following conversion:
Trans-1,2-diphenyl ethylene → Cis-1,2-diphenyl acetylene
Solution
The preparation of alkynes from alkenes requires the use of a halogenating agent and mainly bromine is used for the purpose resulting to the formation of a dihaloalkane and next the alkane is protonated resulting in double elimination and forming the triple bond.
Complete step-by-step answer: When Trans-1,2-diphenyl ethylene is treated with bromine in presence of carbon tetrachloride, then the bromine molecule gets dissociated to get attached to the double bond leading to the forming of the dibromide of the alkene in which both the bromine atoms are in trans position with respect to each other as in a vicinal dihalide.
In the presence of a strong base such as the alcoholic KOH, the desired alkyne will be formed due to the double elimination reaction following the E2 pathway. In this mechanism, the base abstracts the proton that is in anti-position with respect to the any of the bromine atoms and thus the available electrons form the triple bond between the carbon atoms and the other bromine atoms leaves as a leaving group.
The mechanism of the same can be shown as follows:
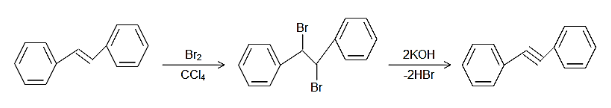
Note: In the double bond in the alkenes, the bromine in carbon tetrachloride adds across the double bond by anti-addition and the solvent used in the reaction which is carbon tetrachloride has no other role to play but just to dissolve the bromine liquid. It has no effect on the reactants. The use of alcohol along with potassium hydroxide also serves the same purpose.
