Question
Question: Both \(C{O_2}\) and \({H_2}O\) contain polar covalent bonds but \(C{O_2}\) is non-polar while \({H...
Both CO2 and H2O contain polar covalent bonds but CO2 is non-polar while H2O is polar because:
A. H atom is smaller than C atom
B. CO2 is a linear molecule while H2O is an angular molecule
C. O−H bond is more polar than C−O bond
D. CO2 contains multiple bonds while H2O has only single bonds
Solution
To solve this question, we must first understand some basic concepts about polarity and Covalent bonds. Then we need to assess the concept of Polar Covalent bond in such a way that we may conclude the correct reason behind the given statement and then only we can conclude the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer: Polar Covalent bond: Basically, a polar bond is a certain class of a covalent bond. A polar covalent bond is a bond that exists between two atoms consisting of electrons that are unevenly distributed. Due to this state, the molecules tend to have some electrical dipole moment wherein the two ends are either slightly positive or negative.
Electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract a shared pair of an electron towards itself. It has no units, it is a tendency. The covalent bond formed between two atoms in molecules whose electronegative difference exists is known as a polar covalent bond.
Step 1: The structure of are as follows:
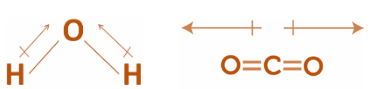
Step 2: By Going through the above explanation and considering the structure of both CO2 and H2O , we may conclude that:
In the structure of CO2 , the arrangement is a liner kind of linear arrangement in which polar bonds are arranged in such a way that the C−O bond polarities cancel each other.
Whereas, in the structure of H2O molecules, the arrangement is a linear kind of angular arrangement O−H bond polarities do not cancel one another.
Step 3: Hence we can conclude that the most correct reason will be:
CO2 is a linear molecule while H2O is an angular molecule
And therefore, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: The polarity of a covalent bond can be explained by a physical quantity called Dipole moment (μ) . The dipole moment is defined as the product of charge and distance of separation of charge.
