Question
Question: Benzene on ozonolysis followed by reaction with \[Zn + {H_2}O\] gives: (A) 3 moles of glycerol (...
Benzene on ozonolysis followed by reaction with Zn+H2O gives:
(A) 3 moles of glycerol
(B) 3 moles of glyoxal
(C) 3 moles of glyoxylic acid
(D) 3 moles of acetylene
Solution
Ozone reacts with carbon-carbon double bonds to give ozonide and reacts with different workup reagents to give products accordingly. Zn+H2O is a reductive work up method, so it will not give oxidized products after ozonide formation.
Complete step by step answer:
Let’s see what will happen as benzene react with ozone.
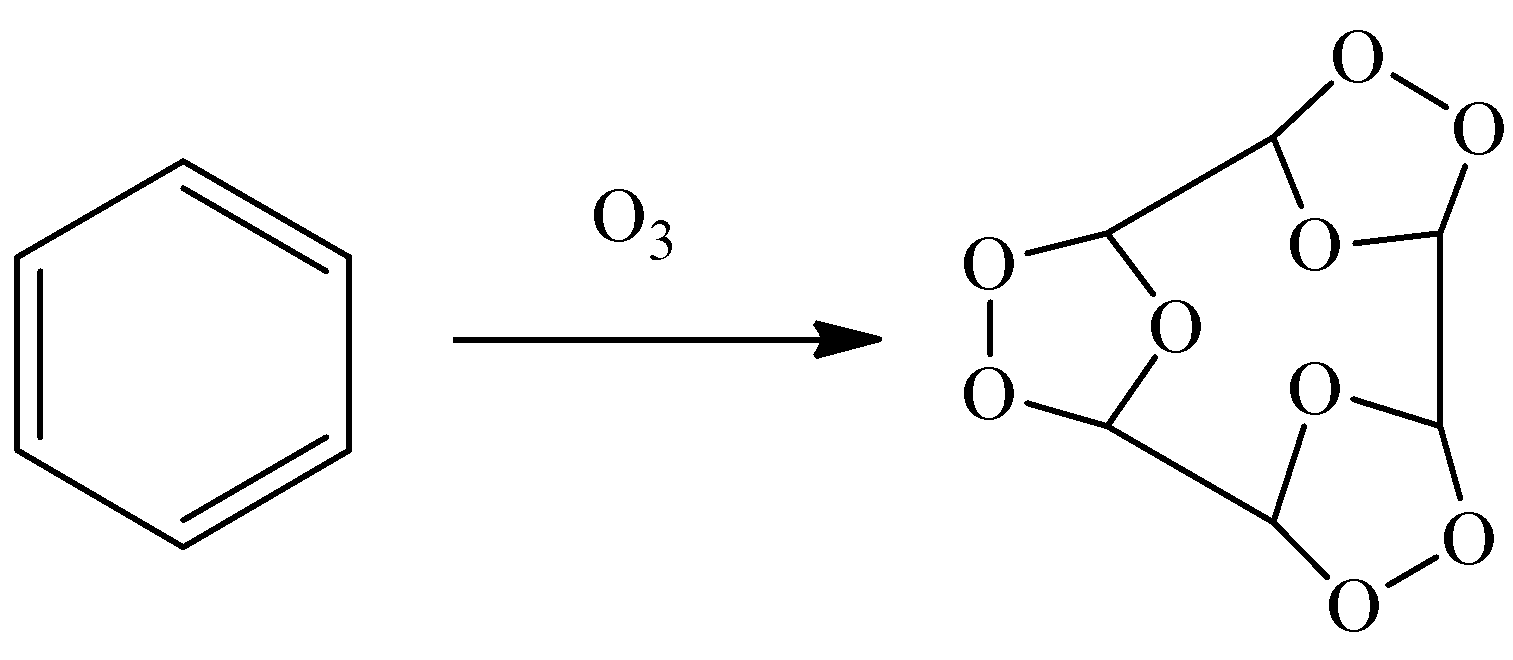
- We can see that benzene will give a triozonide derivative as all three of the double bonds will react with one molecule of ozone. This triozonide intermediate is the stable intermediate formed during this reaction.
- Then we will add Zn+H2O in the solution. As Zn metal is a reducing agent, the workup we do here is called reductive workup. So, whenever reductive workup is done on ozonide intermediate, the two carbon atoms that are bonded to oxygen atoms in the ozonide group, get converted to aldehyde functional groups as shown below.
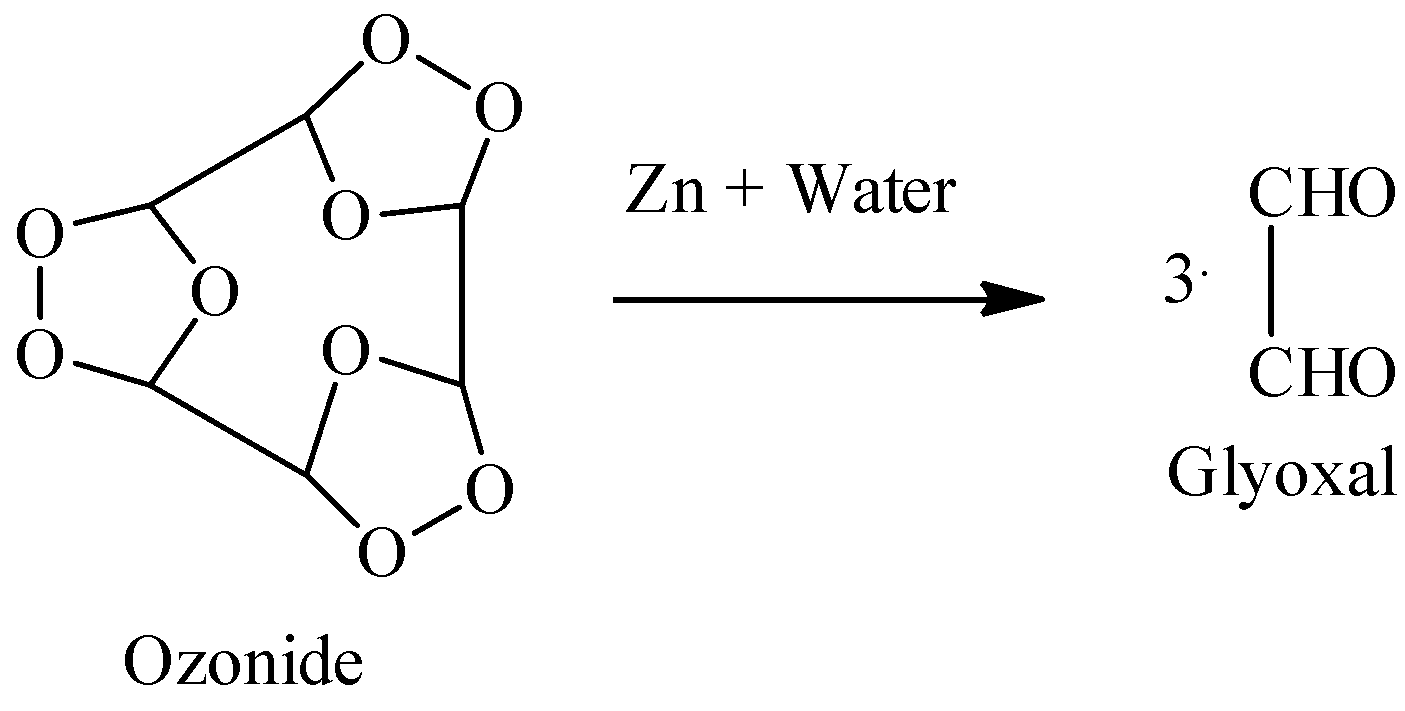
Hence, we get 3 molecules of Glyoxal as a product in this reaction.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Additional Information:
- Zn+H2O and Zn + AcOH is a reductive workup condition. They will give an aldehyde functional group on the carbons bearing oxygen atoms in ozonide.
- Any peroxide or per-acid is an oxidizing workup condition and it will oxidize the carbons further to the carboxylic acid group in the products.
Note: Remember that here all the three double bonds are chemically same and all three will react with ozone. As Zn+H2O is a reductive workup reagent, remember that it does not give an oxidized product, instead it gives carbon bearing aldehyde functionality.
