Question
Question: \(BC{l_3}\) is a planar molecule, while \(NC{l_3}\) is pyramidal, because : a.) N—Cl bond is more ...
BCl3 is a planar molecule, while NCl3 is pyramidal, because :
a.) N—Cl bond is more covalent than B—Cl bond.
b.) Nitrogen atom is smaller than boron atom
c.) B—Cl bond is more polar than N—Cl bond.
d.) BCl3 has no lone pair of electrons but NCl3 has a lone pair of electrons.
Solution
Boron is electron deficient species while nitrogen is not. BCl3 has sp2 hybridisation with electronic configuration of boron = 1s22s22p1while NCl3 has sp3 hybridisation with electronic configuration of N = 1s22s22p3.
Complete answer:
To get the answer to this, we need to know about planar and pyramidal shapes.
Planar is the geometry when all atoms are in the same plane while pyramidal shape comes under tetrahedral geometry. The tetrahedral geometry involves four ligands present tetrahedrally w.r.t. the central metal atom. They have bond angle of 109.40 between adjacent ligands.
If we see BCl3 and NCl3, then the Boron atom has electronic configuration as-
B = 1s22s22p1
The 2s and 2p orbital will hybridise giving sp2 hybrid orbitals that will form bonds with chlorine atoms. The boron with sp2 hybridisation has three bond pairs and no lone pair. So, these three bond pairs form planar structure with 1200 bond angle.
In case of NCl3, the nitrogen atom has electronic configuration as-
N = 1s22s22p3
The 2s and 2p orbitals of nitrogen hybridise giving four sp3 hybrid orbitals that will form bond pairs with chlorine. The nitrogen with sp3 hybridisation has three bond pairs and one lone pair. In actuality, it has tetrahedral geometry with three sides of the tetrahedral having a bond pair and one side there is lone pair. On ignoring the lone pair, visibly the structure is of pyramid shape. Thus, named so.
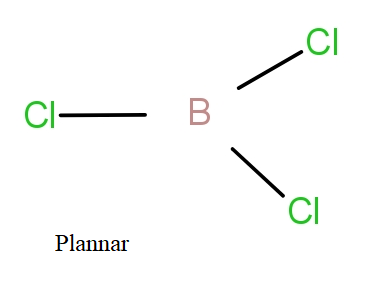
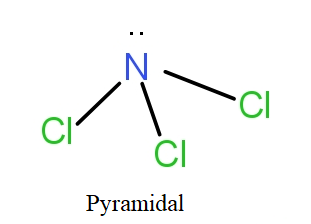
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The geometry and shape of a molecule depends upon the number of bond pairs and number of lone pairs present in the molecule. There are bond pair-bond pair repulsions, bond pair-lone pair repulsions and lone pair-lone pair repulsions which may distort the geometry giving new shapes.
