Question
Question: Back bonding in \[B{{F}_{3}}\] does not affect: a.) Planarity, lewis acid strength and bond angle....
Back bonding in BF3 does not affect:
a.) Planarity, lewis acid strength and bond angle.
b.) Bond length, hybridisation and bond strength.
c.) Bond angle, planarity and geometry.
d.) Lewis acidity, bond length, bond order (B→F).
Solution
Hint : BF3 has a trigonal planar structure and all the 3 B→F bonds lie in the same plane. Therefore all the p orbitals of boron and fluorine are parallel to each other.
Complete step by step solution :
Let us discuss how back bonding occurs in BF3 molecules.
-BF3 molecule has 2p orbitals of each fluorine which has fully filled orbitals and one of the 2p orbital of boron atoms is vacant.
-There will be a lateral overlap between the 2p orbitals involved in the formation of B→F bond. This would result in the transfer of fluorine electrons into the vacant orbitals of the boron atom.
-There is an effective overlap between them because both the orbitals are of the same energy. We can say that an additional pπ−pπ bond is formed and the B→F bond acquires a double bond character.
-Due to this back donation, the electron deficiency of boron is compensated and therefore Lewis acidity of BF3 decreases.
-The tendency of pπ−pπ bond formation is seen maximum in BF3 molecules.
-BF3 molecule forms a resonating structure. The lone pair of electrons between the boron and fluorine resonate giving it 3 resonating structures.
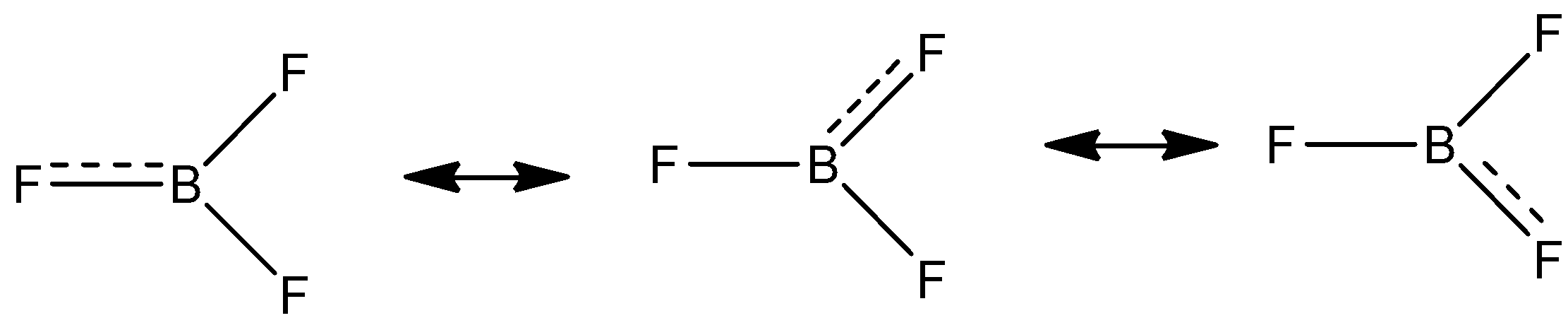
Back bonding BF3 does not affect the bond angle, planarity and the geometry of the molecule.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note : We should keep in mind that due to back bonding the hybridisation changes, bond strength increases and also bond length decreases. It is due to BF3 molecules planar structure and its bond angle, the overlapping of p orbitals occur.
