Question
Question: \(B{{\left( OH \right)}_{3}}\) is a: A. Lewis acid B. Lewis base C. Bronsted base D. Bronste...
B(OH)3 is a:
A. Lewis acid
B. Lewis base
C. Bronsted base
D. Bronsted acid
Solution
Think about the electronic configuration of boron and how the electrons interact when boron forms a bond with the hydroxide ions. Consider the definitions of all the options given to understand the type of compound boric acid is.
Complete Solution :
- Boric acid is obtained when a hot and concentrated solution of borax reacts with strong acids like hydrochloric acid or sulphuric acid. The resulting solution after concentration and cooling gives crystals of boric acid.
- The hydrolysis of compounds of boron like halides, hydrides and nitrides also yields boric acid. It is a white crystalline solid with a soft soapy touch. It is slightly soluble in cold water but almost completely soluble in hot water.
- A Lewis acid is a compound that can accommodate one electron pair. And the compound that can donate a pair of electrons will be known as Lewis base. A Bronsted acid is a molecule that can donate a proton and a Bronsted base is a molecule that can accept a proton.
- Boric acid is a very weak, monobasic acid and does not act as a proton donor. However due to small size of B and presence of only six electrons in its valence shell, B(OH)3 behaves as a Lewis acid, by accepting a pair of electrons from hydroxyl ions of water thereby releasing a proton. The structure of boric acid is:
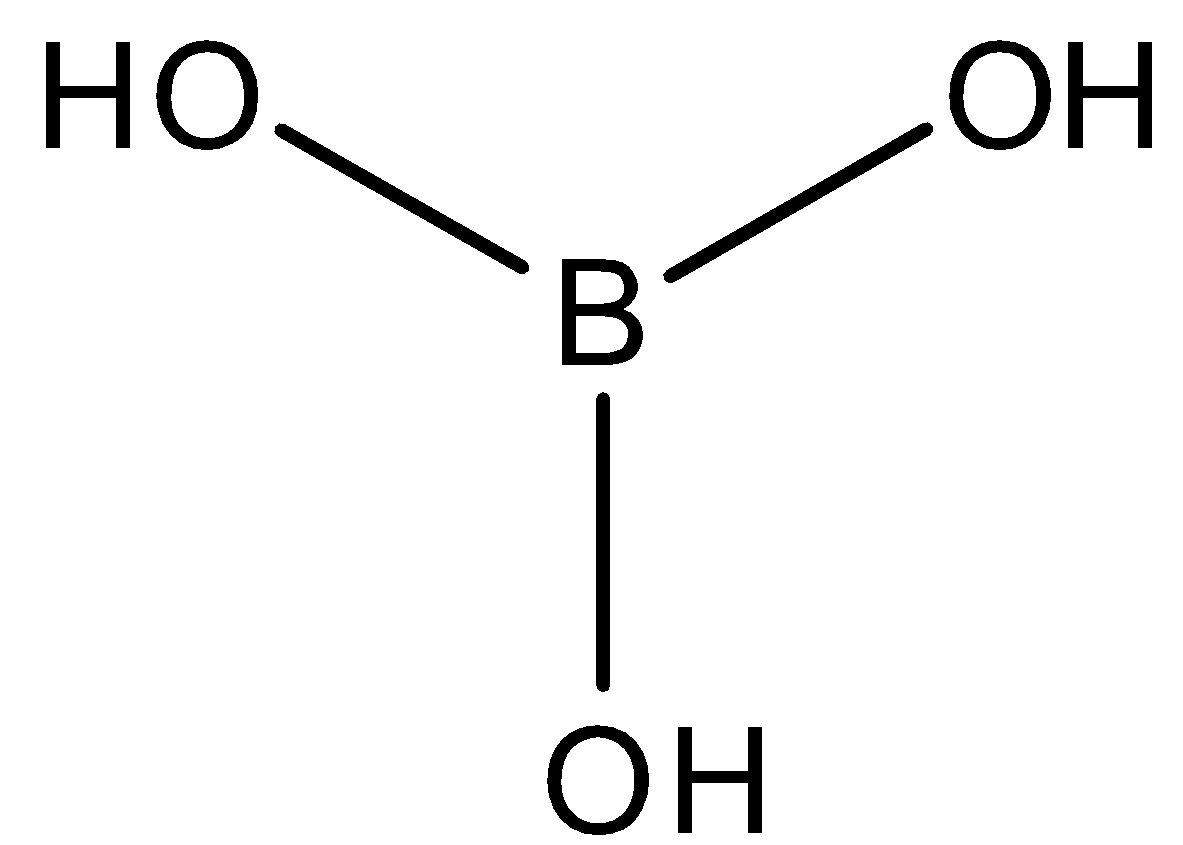
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: Note that the Lewis definition is a generalization of the Bronsted definition. If a compound is a Bronsted base it will almost always be a Lewis base, similarly, a Bronsted acid will be a Lewis acid. But the opposite may not always be true, a molecule that receives an electron pair may not always lose a proton.
