Question
Question: \({{B}_{2}}{{H}_{6}}+N{{H}_{3}}\to \)Addition compound (X) \((X)\xrightarrow{450k}Y+Z(g)\) In t...
B2H6+NH3→Addition compound (X)
(X)450kY+Z(g)
In the above sequence Y and Z are respectively:
(A)- borazine, H2O
(B)- boron, H2
(C)- boron nitride, H2
(D)- borazine and hydrogen
Solution
The addition product formed by the action of ammonia (NH3) on diborane (B2H6) diammoniate of diborane., i.e. B2H6.2NH3. It is ionic in nature. Reaction of B2H6 with NH3 is one of the methods used for the synthesis of borazine.
Complete step by step answer:
The products of the reaction of diborane (B2H6) with ammonia (NH3) depends on the reaction conditions.
At low temperature, B2H6 reacts with NH3 to form an addition product. The chemical reaction is given below:
B2H6+2NH3→B2H6.2NH3
B2H6.2NH3 is ionic in nature and exists as [H3N→BH2←NH3]+[BH4]− .
When the reaction between B2H6 and NH3 is carried out around 450 K temperature, the addition product formed gets converted into borazine and hydrogen. The sequence of chemical reactions taking place is given below:
B2H6+2NH3→B2H6.2NH33B2H6.2NH3450K2B3N3H6+12H2(g)
Since B2H6.2NH3 is unstable at 450 K and only appears as an intermediate in the reaction, we can also write the overall reaction as
3B2H6+6NH3→2B3N3H6+12H2
We can identify the compound Y and Z from the above sequence of reactions. Compound Y is borazine (B3N3H6) and compound Z is hydrogen (H2) gas.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
Borazine is known as inorganic benzene because its structure is similar to that of benzene.
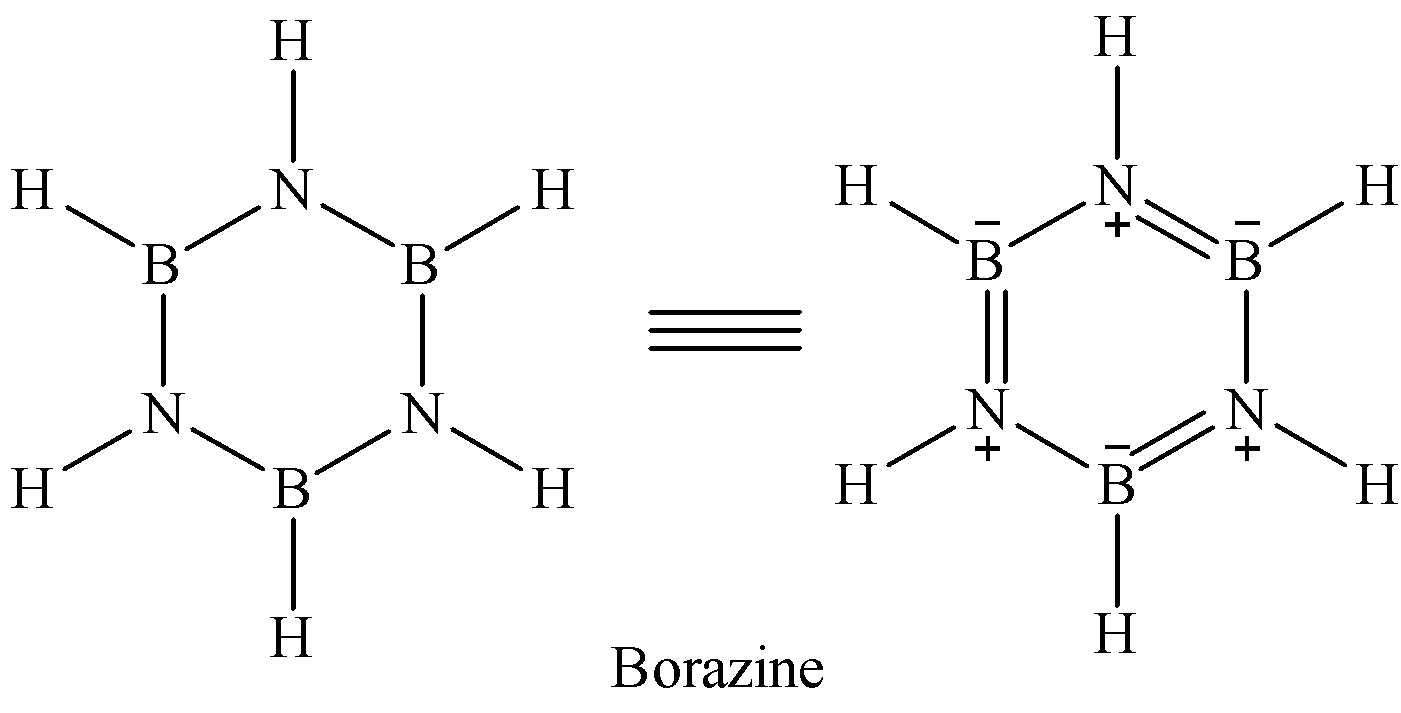
Note: We might get confused between the options. So remember that diborane only forms boron nitride if it is treated with excess of ammonia at high temperature. Thus, here option C cannot be correct. And since there is no oxygen involved in the reaction, option A is also not correct.
