Question
Question: Azulene is antiaromatic. 
Solution
There are some necessary conditions for the compounds to be aromatic. The compound should have a single cyclic cloud of delocalized π−electrons, the compound must be planar, and it should contain (4n+2)π−electrons where n = 1, 2, 3…....etc.
Complete step by step answer:
Based on the molecular orbital theory, Hukel has predicted that electrons in cyclic conjugated polyenes (cyclic polyenes having alternate single and double bonds) containing (4n+2)π−electrons where n = 1, 2, 3, 4, ….etc are completely delocalized. This makes the compound stable and such compounds are called aromatic compounds.
So the necessary and sufficient conditions for the compound to aromatic are that it should have a single cyclic cloud of delocalized π−electrons above and below the plane of the molecule, the compound must be planar, and the compound must contain (4n+2)π−electrons where n = 1, 2, 3, …….etc.
The molecule that doesn't satisfy any one or more of the above conditions then is non-aromatic.
And if the compound is having (4n)π−electronsthen the compound is antiaromatic.
So, in Azulene there are 5 double bonds which means that it has 10 π−electrons as shown below:
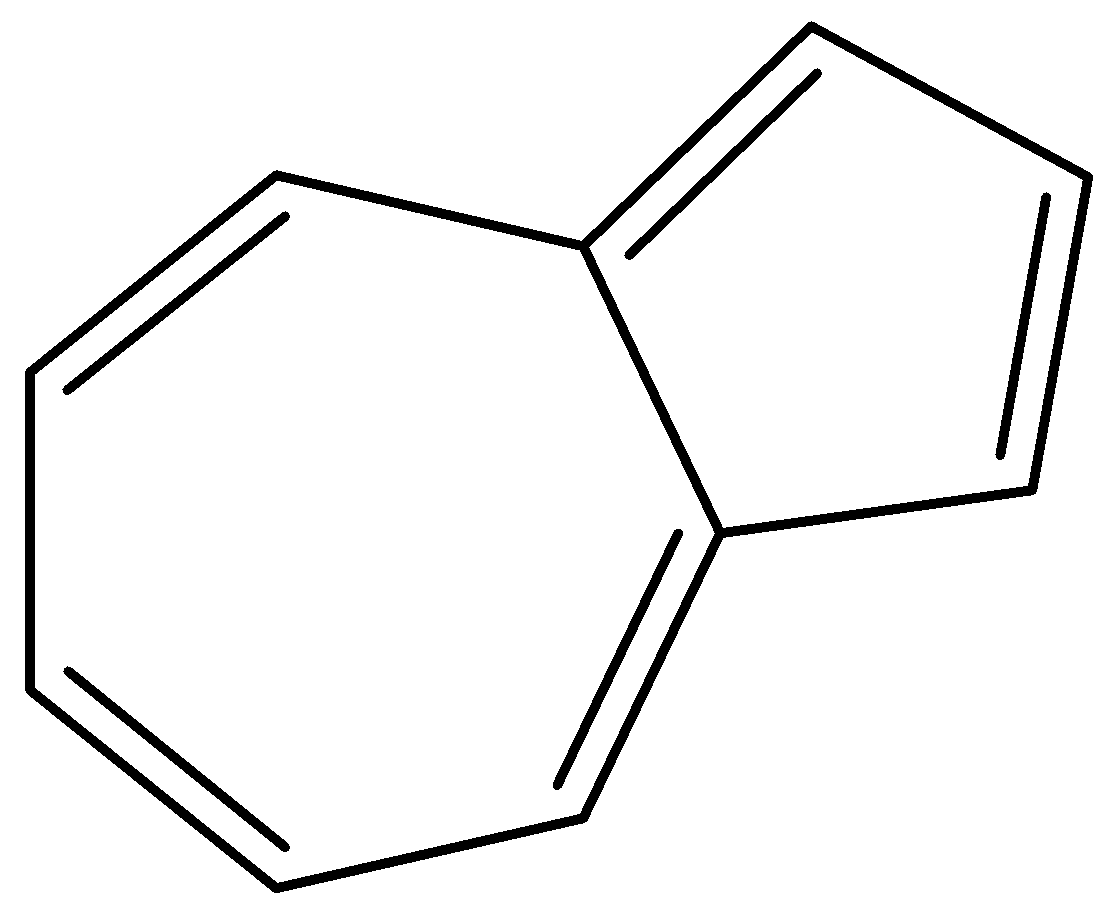
So, when we put n as 2 in the equation of aromatic compound, we get:
(4n+2) π−electrons
(4(2)+2) π−electrons
10π−electrons
So, the Azulene compound is aromatic, not antiaromatic and it will give all the reactions of an aromatic compound. Thus the statement is false.
Note: The 10π−electrons in Azulene is contributed by two aromatic ions, by tropylium cation and the cyclopentadienyl anion. Azulene gives Friedel-Crafts-like reactions and both its peripheral bonds have the same length.
