Question
Question: Azoxybenzene can be obtained by the treatment of nitro-benzene with: A.\[{{O}_{2}}\] B.\[{{H}_{2...
Azoxybenzene can be obtained by the treatment of nitro-benzene with:
A.O2
B.H2/Pt
C.Na3As2O3/NaOH
D.Zn/NaOH
Solution
Azobenzene is made by using two molecules of nitrobenzene, and the two nitrogens are attached to each other by a double bond.
In this conversion process, the reduction of nitrobenzene takes place.
Complete step by step answer:
The structure of nitrobenzene has a nitro group attached to the benzene ring. Nitrobenzene is an organic compound which has the chemical formula C6H5NO2. It is water-insoluble, and has pale yellow oil type texture with an almond-like odour. It freezes in order to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a huge scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents.
The word azoxy means that the compound contains a nitrogen-nitrogen double bond as well as a nitrogen oxygen bond. They are considered as N−oxides of azo compounds. Azoxy compounds are 1,3−dipoles. They undergo 1,3 dipolar cycloaddition with double bonds. Most compounds containing azoxy have aryl substituents. They are normally prepared by reduction of nitro compounds, such as the reduction of nitrobenzene with the help of arsenous oxide to azoxybenzene.
Azoxybenzene is an organic compound with the formula C6H5N(O)NC6H5. It is a yellow, low-melting solid. The molecule has a planar C2N2O core.
The structure of nitrobenzene and azobenzene is shown the given diagram below.
This diagram depicts the conversion of nitrobenzene to azoxybenzene by the use of Na3As2O3/NaOH as a reagent.
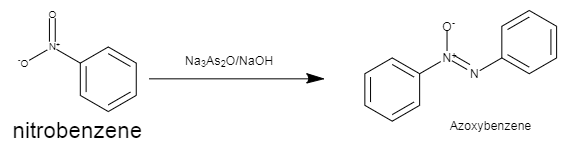
A detailed mechanism of the reaction is explained below.
In this process, Nitrobenzene first reduces to nitrobenzene and N−hydroxyaniline. Some of the nitrobenzene could further get reduced to aniline and N−phenylhydroxylamine, both of which are termed as nucleophiles and can react with the nitroso N=O bond (which is analogous to a carbonyl). Elimination of water in both reactions results in formation of azobenzene and azobenzene respectively.
So the correct option is C.
Note: Nitrobenzene is a toxic chemical with a number of harmful effects
-Acute inhalation, or oral, and dermal exposure to nitrobenzene in human beings produces a condition called methemoglobinemia, in which hemoglobin in blood, is converted to methemoglobin, which results in lowering in the amount of oxygen released to the tissues of the human body.
