Question
Question: At what rate is electrical energy converted into thermal energy in the resistance of the bar after t...
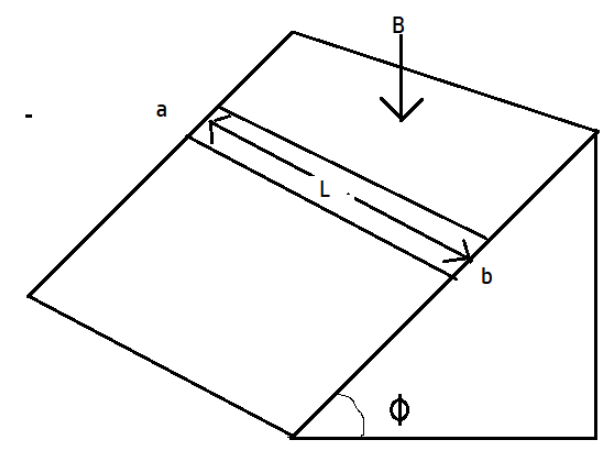
At what rate is electrical energy converted into thermal energy in the resistance of the bar after the terminal velocity has been reached?
(A) 2RB2l2vcos2ϕ
(B) RB2l2vcos2ϕ
(C) RB2l2vsin2ϕ
(D) 2RB2l2vsin2ϕ
Solution
Here metal rod of length l, is in motion in the area where there is a magnetic field present. We know from Maxwell equations that a changing magnetic field can induce current whose direction is given by Lenz law. Also, if the magnetic flux remains constant then there will be no induced emf.
Complete step by step answer:
From the concept of motional emf, the emf induced in a conductor which is moving in the region where the magnetic field is present. So, let us find the magnetic flux,
⇒ϕB=B.A=BAcosφ
The area which the conductor covers can be written as the product of velocity and length, so, the equation becomes
⇒e=Blvcosϕ
But we are interested in finding out the rate at which the electrical energy converted into thermal energy in the resistance of the bar after the terminal velocity has been reached.
So, we need to find the rate of generation of thermal energy.
Using the formula,
⇒P=RV2 where V is the emf generated and R is the resistance of the conductor.
∴P=RB2l2v2cos2ϕ
So, the correct option is (B).
Note: If there was no change in the magnetic flux then there would have been no emf induced in the conductor. Since flux is the dot product of magnetic field and area vector, to change the flux there can be three conditions:
- Change in a magnetic field.
-Change in the area of the conductor.
-Change in the angle between the magnetic field and the area vector.
