Question
Question: At what angle a ball should be thrown with a velocity of \(24{\text{ }}m{s^{ - 1}}\) just to cross a...
At what angle a ball should be thrown with a velocity of 24 ms−1 just to cross a wall 16 m high at a horizontal distance of 32 m. Given g=10 ms−2.
Solution
The motion of the ball is in projectile. We have to formulate equations for both horizontal direction and vertical direction. Then by solving the equation we will formulate another quadratic equation, from which we will find the value of angle of projection.
Complete step by step answer:
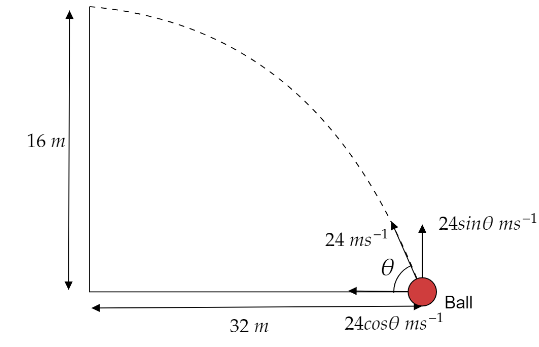
According to the question the ball has to just cross the height 16 m.
So, we consider the height y=16 m.
Let the horizontal distance be x which is given as 32 m.
The velocity of the particle u is given as 24 ms−1.
Let θ be the angle of inclination.So, the horizontal velocity is 24cosθ and the vertical velocity is 24sinθ. Let us formulate the equation for horizontal axis as,
s=ut+21at2 where s=x=32 m, u=24cosθ and a=0 for horizontal direction in projectile motion.
Substituting the values we get,
32=24cosθ×t
Formulating the equation terms of t we get,
t=34secθ−−−−−(1)
Now, its time to formulate the equation in vertical axis,
s=ut+21at2 where s=y=16 m, u=24sinθ, a=−g=−10 ms−2
So, by substituting the values in the equation we get,
16=24sinθ×t−21×10×t2
Substituting the value of t from equation (1) we get,
16=24sinθ×34secθ−21×10×(34secθ)2
Simplifying the equation we get,
16=32tanθ−980sec2θ
Converting sec2θ=1+tan2θ and dividing the whole equation with 16 we get,
⇒1=2tanθ−95(1+tan2θ)
Again, simplifying the equation we get,
9=18tanθ−5−5tan2θ
By, arranging the equation in quadratic form we get,
5tan2θ−18tanθ+14=0
From Sreedhar Acharya’s formula we get,
tanθ=2×518±324−4×5×14=1018±44
Thus we get the values of tanθ while considering positive value is,
tanθ=2.4633
While considering negative value we get,
∴tanθ=1.1367
Thus, the values of θ are 23.24∘ and 50.39∘.
Note: It must be noted that in order the ball should just cross the wall the angle must be a little greater than either 23.24∘ or 50.39∘. We consider the uniform motion of a body in projectile motion so the acceleration in the horizontal axis is zero.
