Question
Question: At high concentration of soap in water, soap will behave as: A.Molecular solid B.Associated coll...
At high concentration of soap in water, soap will behave as:
A.Molecular solid
B.Associated colloid
C.Macromolecular colloid
D.Lyophilic colloid
Solution
Soap is mainly made up of triglycerides and an alkaline strong base such as sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. Hard soap is made of sodium as a base whereas soft soap is made up of potassium as a base. So in this we will see the reaction on how soap is made from sodium and potassium as a base.
Complete step by step answer:
At low concentration soap behaves as a normal electrolyte whereas in case of high concentration it acts as an ionic micelles.
Reaction of soap when it dissolves in water at low concentrations is as follows:
RCOONa→RCOO−+Na+
It dissociates to give RCOO− and Na+ .
So, at low concentrations carboxylate ion dissociates into two parts RCOO−
a) The part that loves water(hydrophilic): COO−
b) Part that hates water(hydrophobic): R
So,here is an example of sodium stearate soapC17H35COO−Na+
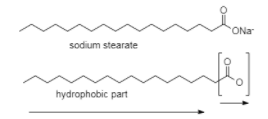
At lower concentrations the head part that is the carboxylate ion COO− dissolves in the water whereas the tail part that is R stays on the surface.
Now, from all this we can say that at lower concentrations soap acts as an electrolyte.
Associated colloids are those substances that behave as normal electrolytes at low concentrations whereas in higher concentrations it behaves as a colloidal particle.
So, from this we can say that the soap behaves as associated colloids at higher concentrations.
So, the correct answer is option B i.e Associated colloid.
Note:
The concentration range at which a soap makes a micelles is known as critical micelle concentration (cmc). It ranges from 10−4−10−3mol/L . The soaps which are made of sodium and potassium as base are only used for cleaning purposes.
