Question
Question: At a given instant, A is moving with velocity of 5 m/s upwards. What is velocity of B at that time- ...
At a given instant, A is moving with velocity of 5 m/s upwards. What is velocity of B at that time-
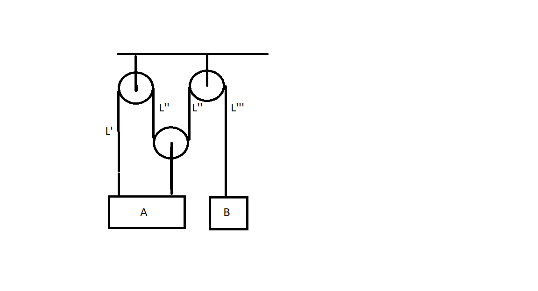
Solution
Hint
According to the question A block is moving upward direction with velocity of 5m/s. Now according to the picture we assume that the rope is continuous. In the first part of the picture the length of the string is L’ then the middle part of the strings are L’’ each and the last part of the string is L”’.
Complete step by step answer
as the rope is continuous thats why
⇒L′+2L′′+L′′′=l … [where l is constant]........equation 1
Now, differential equation 1 with respect to time we get,
⇒dtdL′+2dtdL′′+dtdL′′′=0. ...............[because, l is constant]
Now, dtdL′ let the velocity of block A which is upward direction is vA and dtdL′′ is equal to vA
Now,
⇒vA+2vA+dtdL′′′=0. ...........[where dL’’’/dt is velocity of block b]
Putting the value of vA we get,
⇒5+(2×5)=−dtdL′′′=vB
⇒vB=15m/s
Here vB is the velocity of block B.
Because the sign is negative the velocity of block B is in downward direction vA
vB = 15m/s (downward direction).
Note
The sign convention is the most important part in this type of question. Sign convention is a set of rules to set signs for image distance, object distance, focal length, etc for mathematical analysis of image formation.
