Question
Question: Assume the bottom of a \(16ft\) ladder is pulled out at a rate of \(3ft/s\). How do you find the rat...
Assume the bottom of a 16ft ladder is pulled out at a rate of 3ft/s. How do you find the rate at the top of the ladder when it is 10ft from the ground?
Solution
To solve this question, we need to use the Pythagoras theorem. On substituting the values of the length and the height of the ladder, we will get the horizontal distance of the bottom end of the ladder from the top point. Then on differentiating the equation obtained after applying the Pythagoras theorem, we will get a relation between the speeds of the top and the bottom points. In that relation, we have to substitute the given height, and the obtained horizontal distance to get the final rate at the top.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us label the ladder as AB whose top end is at the point A and the bottom is at the point B. Let us assume the speed of the point A to be v. We represent these in the below figure.
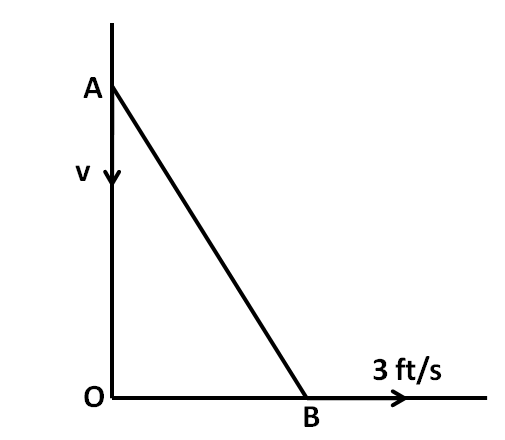
Let us apply Pythagoras theorem in the triangle OAB to get
⇒AB2=OA2+OB2......(i)
According to the question, the length of the ladder is AB=16ft, and the height of the ladder from the ground is given as to be equal to 10ft, which means that OA=10ft. Therefore, we substitute AB=16ft and OA=10ft in the above equation to get
⇒162=102+OB2⇒256=100+OB2
Subtracting 100 from both the sides, we get
